

ABSTRACT: The Swordfish NVMe Model Overview and Mapping Guide defines the model to manage NVMe and NVMe-oF storage systems with Redfish and Swordfish. It provides the detailed mapping information between the NVMe, NVMe-oF specifications and the Redfish and Swordfish specifications.
Publication of this Working Draft for review and comment has been approved by the Scalable Storage Management Technical Work Group. This draft represents a ‘best effort’ attempt by the Scalable Storage Management Technical Work Group to reach preliminary consensus, and it may be updated, replaced, or made obsolete at any time. This document should not be used as reference material or cited as other than a ‘work in progress.’ Suggestions for revision should be directed to http://www.snia.org/feedback.
Copyright (c) 2020 SNIA. All rights reserved. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The SNIA hereby grants permission for individuals to use this document for personal use only, and for corporations and other business entities to use this document for internal use only (including internal copying, distribution, and display) provided that:
Any text, diagram, chart, table or definition reproduced must be reproduced in its entirety with no alteration, and,
Any document, printed or electronic, in which material from this document (or any portion hereof) is reproduced must acknowledge the SNIA copyright on that material, and must credit the SNIA for granting permission for its reuse.
Other than as explicitly provided above, you may not make any commercial use of this document, or any portion thereof, or distribute this document to third parties. All rights not explicitly granted are expressly reserved to SNIA.
Permission to use this document for purposes other than those enumerated above may be requested by emailing tcmd@snia.org. Please include the identity of the requesting individual and/or company and a brief description of the purpose, nature, and scope of the requested use.
All code fragments, scripts, data tables, and sample code in this SNIA document are made available under the following license:
BSD 3-Clause Software License
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Neither the name of The Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
The information contained in this publication is subject to change without notice. The SNIA makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this specification, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. The SNIA shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use.
Suggestions for revisions should be directed to http://www.snia.org/feedback/.
Revisions to this document are summarized in Table 1.
| Date | Revision | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 18 August 2020 | 1.2.1 | Initial Release |
SNIA is actively engaged in expanding and refining the Swordfish specification. The most current revision can be found on the SNIA web site at https://www.snia.org/tech_activities/standards/curr_standards/swordfish.
Current SNIA practice is to make updates and other information available through their web site at http://www.snia.org.
Requests for interpretation, suggestions for improvement and addenda, or defect reports are welcome. They should be sent via the SNIA Feedback Portal at http://www.snia.org/feedback/ or by mail to the Storage Networking Industry Association, 4360 ArrowsWest Drive, Colorado Springs, Colorado 80907, U.S.A.
This document is intended for use by individuals and companies engaged in storage management.
This document is versioned material. Versioned material shall have a three-level revision identifier, comprised of a version number ‘v’, a release number ‘r’ and an errata number ‘e’. Future publications of this document are subject to specific constraints on the scope of change that is permissible from one revision to the next and the degree of interoperability and backward compatibility that should be assumed between products designed to this standard. This versioning policy applies to all SNIA Swordfish versioned materials.
Version Number: Versioned material having version number ‘v’ shall be backwards compatible with all of revisions of that material that have the same version number ‘v’. There is no assurance of interoperability or backward compatibility between revisions of a versioned material with different version numbers.
Release Number: Versioned material with a version number ‘v’ and release number ‘r’ shall be backwards compatible with previous revisions of the material with the same version number, and a lower release number. A minor revision represents a technical change to existing content or an adjustment to the scope of the versioned material. Each minor revision causes the release number to be increased by one.
Errata Number: Versioned material having version number ‘v’, a release number ‘r’, and an errata number ‘e’ should be backwards compatible with previous revisions of the material with the same version number and release number (“errata versions”). An errata revision of versioned material is limited to minor corrections or clarifications of existing versioned material. An errata revision may be backwards incompatible, if the incompatibility is necessary for correct operation of implementations of the versioned material.
The Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) is a non-profit organization made up of member companies spanning information technology. A globally recognized and trusted authority, SNIA’s mission is to lead the storage industry in developing and promoting vendor-neutral architectures, standards and educational services that facilitate the efficient management, movement and security of information.
The SNIA Scalable Storage Management Technical Work Group, which developed and reviewed this work in progress, would like to recognize the significant contributions made by the members listed in Table 2.
| Member | Representatives |
|---|---|
| Broadcom Inc. | Richelle Ahlvers |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. | Krishnakumar Gowravaram |
| Dell Inc. | David Black Jim Pendergraft Michael Raineri |
| Hewlett Packard Enterprise | Curtis Ballard Jeff Hilland Chris Lionetti |
| Intel Corporation | Rajalaxmi Angadi Phil Cayton Slawek Putyrski |
| Kioxia | Mark Carlson |
| Lenovo | Keith Campbell |
| NetApp, Inc. | Don Deel Fred Knight |
| Samsung Corporation | Lu Fan Bill Martin Tom Rainey |
| VMware, Inc. | Murali Rajagopal |
1. Abstract
2. Scope
2.1. Document Goals
2.2. Audience Assumptions
3. Normative References
3.1. Overview
3.2. Approved references
3.3. References under development
3.4. Other references
4. NVMe Model Overview
4.1. Introduction
4.1.1. Fundamental Model Design Assertions
4.2. Overall NVMe Subsystem Model
4.2.1. Major NVM Objects Mapped to RF/SF
4.2.1.1. NVM Subsystem
4.2.1.2. NVM Controller (IO, Admin and Discovery)
4.2.1.3. Namespace
4.2.1.4. Endurance Group
4.2.1.5. NVM Set
4.2.1.6. NVM Domain
4.2.2. NVM Subsystem Model
4.2.3. NVMe-oF Subsystem Model
5. Example Instances
5.1. Introduction
5.2. Simple SSD
5.2.1. Overview
5.2.2. Explanation of Object use
5.2.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.2.4. Mockup
5.3. Complex SSD
5.3.1. Overview
5.3.2. Explanation of Object use
5.3.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.3.3.1. Mockup
5.4. Simple SSD with IP (NVMe-oF) Attach
5.4.1. Overview
5.4.2. Explanation of Object use
5.4.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.4.4. Mockup
5.5. JBOF
5.5.1. Overview
5.5.2. Explanation of Object use
5.5.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.5.4. Mockup
5.6. Opaque Array
5.6.1. Overview
5.6.2. Explanation of Object use
5.6.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.6.4. Mockup
5.7. Subsystem (Fabric) Model - NVMe-oF: Fabric Attach Subsystem
5.7.1. Overview
5.7.2. Explanation of Object use
5.7.3. Redfish / Swordfish Object Representation
5.7.4. Mockup
5.8. NVMe Domains
5.8.1. Overview
5.8.2. Explanation of Object use
5.8.3. Mockup
6. Property Mapping
6.1. Introduction
6.2. Property Mapping Template
6.3. NVM subsystem
6.3.1. Mockup
6.3.2. Property Mapping
6.3.2.1. Name
6.3.2.2. Description
6.3.2.3. Status.State
6.3.2.4. Status.Health
6.3.2.5. Status.HealthRollup
6.3.2.6. Controllers
6.3.2.7. Identifiers
6.3.2.8. Identifiers.DurableNameFormat
6.3.2.9. Identifiers.DurableName
6.3.2.10. Volumes
6.4. NVM Controllers
6.4.1. Admin Controller
6.4.1.1. Mockup
6.4.1.2. Property Mapping
6.4.1.2.1. Name
6.4.1.2.2. Description
6.4.1.2.3. Status.State
6.4.1.2.4. Status.Health
6.4.1.2.5. SupportControllerProtocols
6.4.1.2.6. NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType
6.4.1.2.7. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion
6.4.1.2.8. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations
6.4.1.2.9. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive
6.4.1.2.10. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState
6.4.1.2.11. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId
6.4.1.2.12. NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize
6.4.1.2.13. NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize
6.4.1.2.14. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded
6.4.2. Discovery Controller
6.4.2.1. Mockup
6.4.2.2. Property Mapping
6.4.2.2.1. Name
6.4.2.2.2. Description
6.4.2.2.3. Status.State
6.4.2.2.4. Status.Health
6.4.2.2.5. SupportControllerProtocols
6.4.2.2.6. NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType
6.4.2.2.7. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion
6.4.2.2.8. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive
6.4.2.2.9. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState
6.4.2.2.10. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId
6.4.2.2.11. NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize
6.4.2.2.12. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded
6.4.2.2.13. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut
6.4.2.2.14. Links.AttchedVolumes
6.4.2.2.15. Links.Endpoints
6.4.2.2.16. Links.Connections
6.4.3. IO Controller
6.4.3.1. Mockup
6.4.3.2. Property Mapping
6.4.3.2.1. Name
6.4.3.2.2. Description
6.4.3.2.3. Status.State
6.4.3.2.4. Status.Health
6.4.3.2.5. SupportControllerProtocols
6.4.3.2.6. NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType
6.4.3.2.7. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion
6.4.3.2.8. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsUUIDList
6.4.3.2.9. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations
6.4.3.2.10. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsNamespaceGranularity
6.4.3.2.11. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive
6.4.3.2.12. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsPredictableLatencyMode
6.4.3.2.13. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsEnduranceGroups
6.4.3.2.14. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsReadRecoveryLevels
6.4.3.2.15. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsNVMSets
6.4.3.2.16. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState
6.4.3.2.17. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId
6.4.3.2.18. NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize
6.4.3.2.19. NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize
6.4.3.2.20. NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.AccessState
6.4.3.2.21. NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.Volume
6.4.3.2.22. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PRMUnreliable
6.4.3.2.23. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PowerBackupFailed
6.4.3.2.24. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.MediaInReadOnly
6.4.3.2.25. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded
6.4.3.2.26. NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut
6.4.3.2.27. Links.AttchedVolumes
6.4.3.2.28. Links.Endpoints
6.4.3.2.29. Links.Connections
6.5. Namespace
6.5.1. Mockup
6.5.2. Property Mapping
6.6. Endurance Group
6.6.1. Mockup
6.6.2. Property Mapping
6.6.2.1. Name
6.6.2.2. Description
6.6.2.3. Status.State
6.6.2.4. Status.Health
6.6.2.5. Capacity.Data.ConsumedBytes
6.6.2.6. Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes
6.6.2.7. CapacitySources
6.6.2.8. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.PredictedMediaLifeLeftPercent
6.6.2.9. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.PercentUsed
6.6.2.10. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.EnduranceEstimate
6.6.2.11. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsRead
6.6.2.12. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsWritten
6.6.2.13. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaUnitsWritten
6.6.2.14. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostReadCommandCount
6.6.2.15. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostWriteCommandCount
6.6.2.16. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaAndDataIntegrityErrorCount
6.6.2.17. NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.ErrorInformationLogEntryCount
6.7. NVM Set
6.7.1. Mockup
6.7.2. Property Mapping
The Swordfish NVMe Model Overview and Mapping Guide defines the model to manage NVMe and NVMe-oF storage systems with Redfish and Swordfish. It provides the detailed mapping information between the NVMe, NVMe-oF specifications and the Redfish and Swordfish specifications.
This document describes how both the NVMe Subsystem model and the NVMe-oF fabric system model should be mapped consistently to Redfish and Swordfish constructs for implementations to be managed within Redfish and Swordfish management environments.
This model and mapping information does not describe or assert any specific implementation recommendation technologies.
This document also provides the mapping information for properties recommended to be implemented in Redfish/Swordfish for NVMe and NVMe-oF devices and the corresponding reference information from the NVMe and NVMe-oF specifications.
This document assumes that the reader of this document is familiar with NVMe and NVMe-oF technologies and concepts. It also assumes the reader has knowledge of the Redfish and Swordfish concepts.
The documents listed in Table 3 are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
None defined in this document.
None defined in this document.
In order to manage NVMe and NVMe-oF devices and systems in a large scale environment, a higher level management ecosystem is needed. The Redfish/Swordfish management specifications are designed to manage multi-system environments, including multiple types of fabrics, covering not only multiple technologies, but also inclusive of system management, storage management and fabric management, making it the ideal ecosystem in which to add not only the integration of NVMe devices for system and storage management, but NVMe-oF for fabric management.
This document describes how both the NVMe Subsystem model and the NVMe-oF fabric system model should be mapped consistently to Redfish and Swordfish constructs for implementations to be managed within Redfish and Swordfish management environments. This model and mapping information does not describe or assert any specific implementation recommendation technologies.
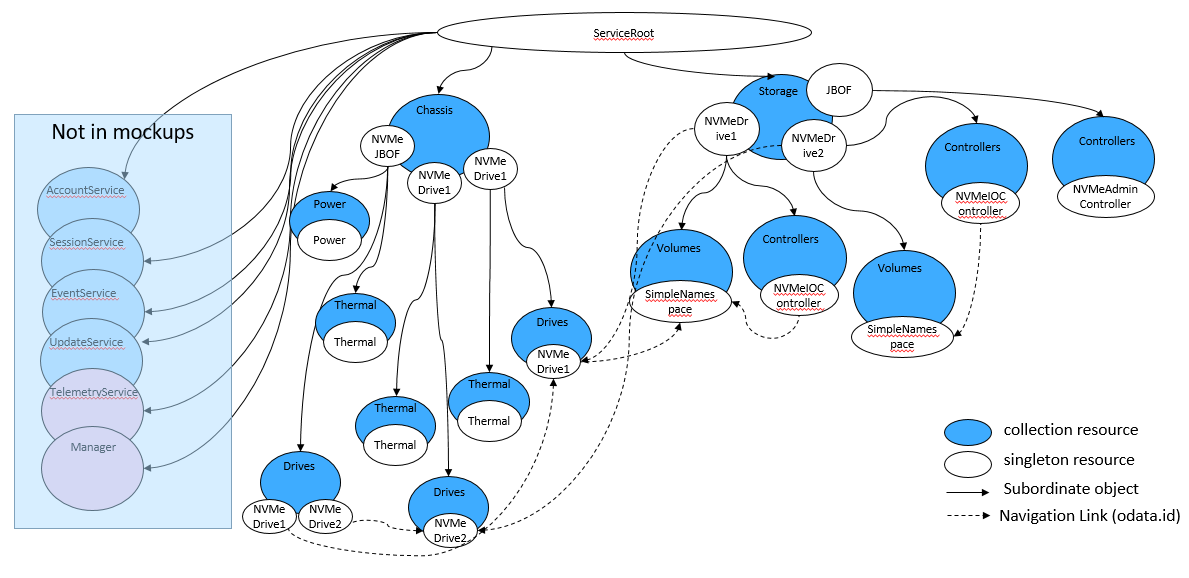
Similar implementations will have similar Redfish and Swordfish constructs. Mockups are used to show static examples of sample representations. Requirements and recommendations for implementations are provided separately through the Swordfish NVMe and NVMe-oF profiles. The profiles use the Redfish interoperability profile schema to specify the required, recommended and optional properties and schema for specific configurations and functionality that correspond to classes of implementations.
There shall be a unified model across all types of NVMe devices.
There shall not be a different model for “drives” vs other types of NVMe devices
The model will cover an appropriate level of abstraction for all types of NVMe devices based on modeling and mockups reflected in the documented permutations (e.g., from simple drives through to complex fabric virtual systems)
The logical model for NVMe-oF shall leverage the NVMe Subsystem model
Logical subsystems, controllers, and namespaces are the same objects with the same relationships as in the NVMe Subystem Model. Unneeded objects are not instantiated (e.g., Endurance Groups, sets)
The NVMe native model should map to the existing Redfish and Swordfish constructs when and where possible
Key Tenets:
Model reflects a unified view of all NVMe device types.
Devices will instantiate an appropriate subset of the model
The model diagrams do not reflect all available schema elements.
Model leverages and coarsely maps to existing (Redfish and) Swordfish storage model
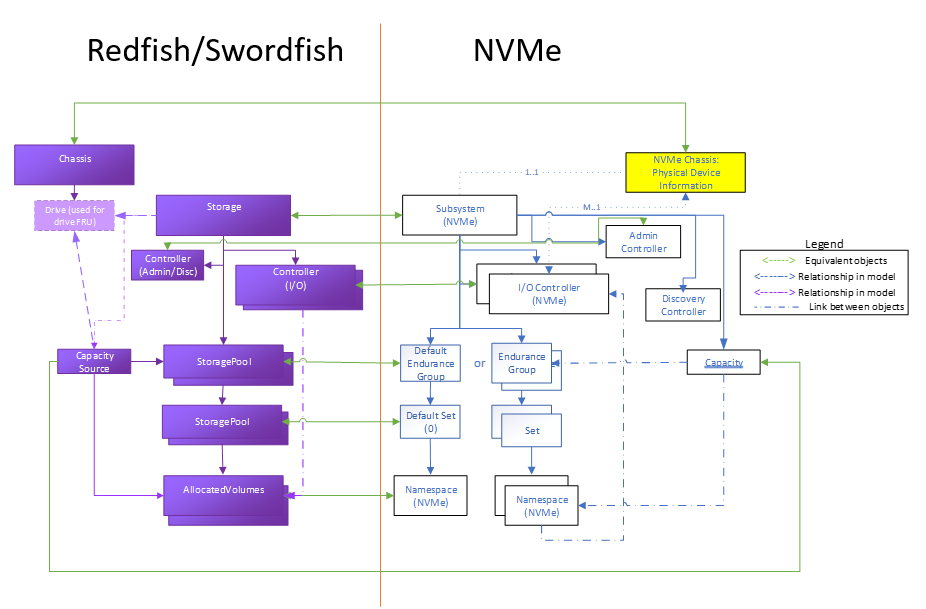
An NVM subsystem includes one or more controllers, zero or more namespaces, and one or more ports. Examples of NVM subsystems include Enterprise and Client systems that utilize PCI Express based solid state drives and/or fabric connectivity.
The interface between a host and an NVM subsystem
Admin controller: controller that exposes capabilities that allow a host to manage an NVM subsystem
Discovery: controller that exposes capabilities that allow a host to retrieve a Discovery Log Page
I/O: controller that implements I/O queues and is intended to be used to access a non-volatile memory storage medium
A quantity of non-volatile memory that may be formatted into logical blocks. When formatted, a namespace of size n is a collection of logical blocks with logical block addresses from 0 to (n-1).
A portion of NVM in the NVM subsystem whose endurance is managed as a group
An NVM Set is a collection of NVM that is separate (logically and potentially physically) from NVM in other NVM Sets.
A domain is the smallest indivisible unit that shares state (e.g., power state, capacity information). Domain members can be NVM controllers, endurance groups, sets or namespaces
The following diagram reflects the high level mapping of the key NVM objects into Redfish / Swordfish schema objects. These largely follow existing relationships used by the Swordfish storage specification for non-NVMe implementations as well, which provides a great deal of consistency for storage clients, as well as for implementations such as NVMe arrays that may be delivering solutions that combine NVMe and other technologies.
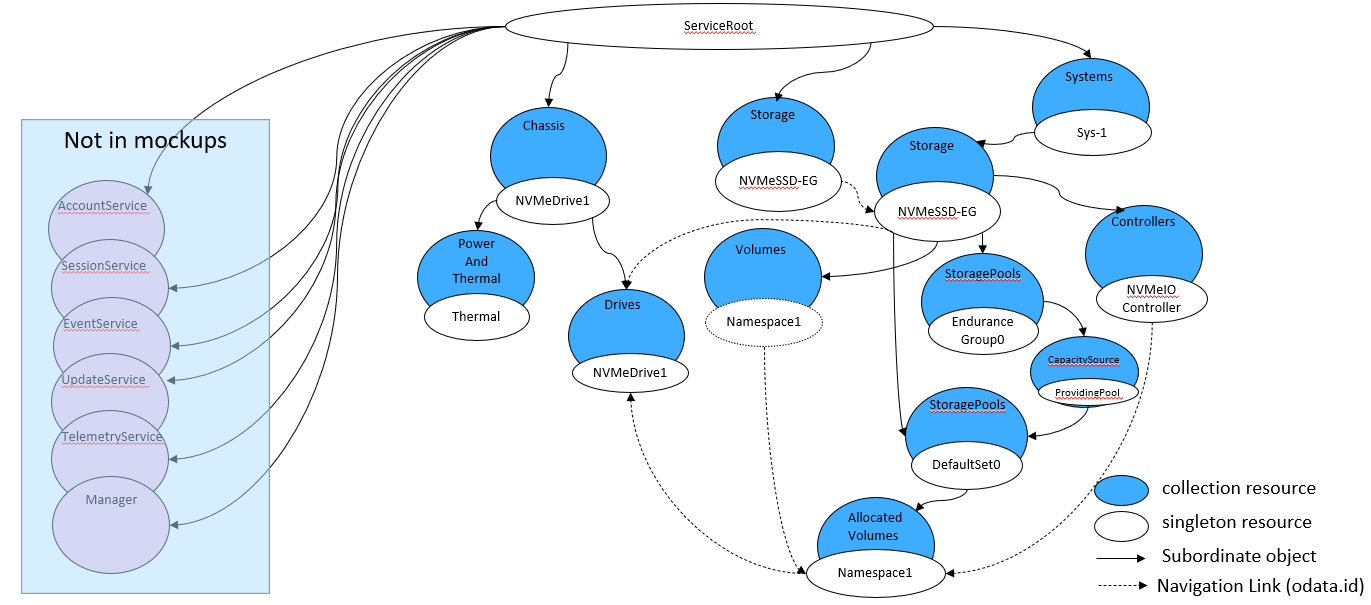
This model covers a wide range of instantiations ranging from individual SSDs, to multi-rack storage systems. All of these can be represented by this NVM Subsystem model, shown in Figure 1.
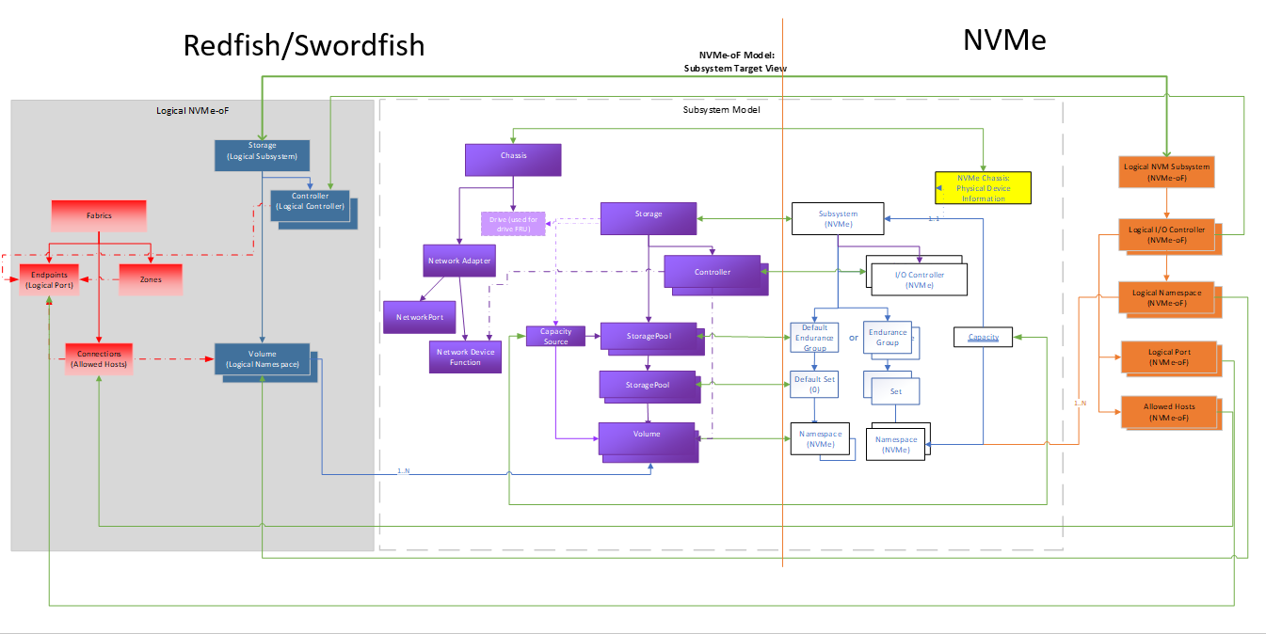
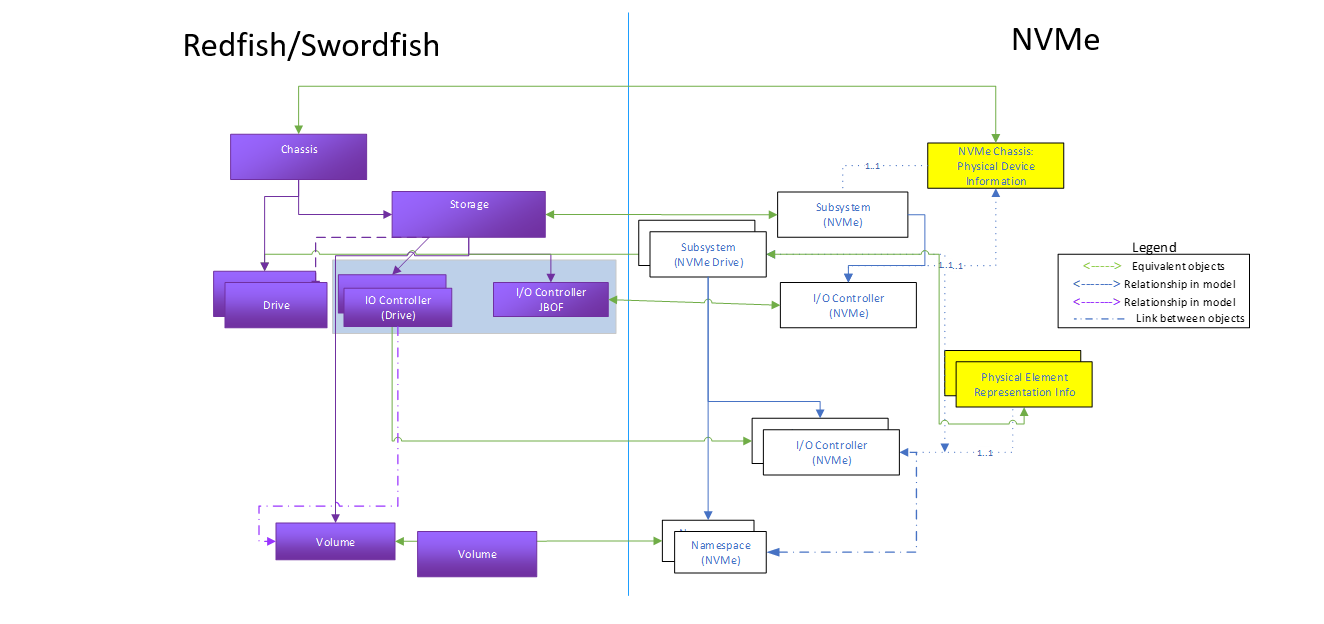
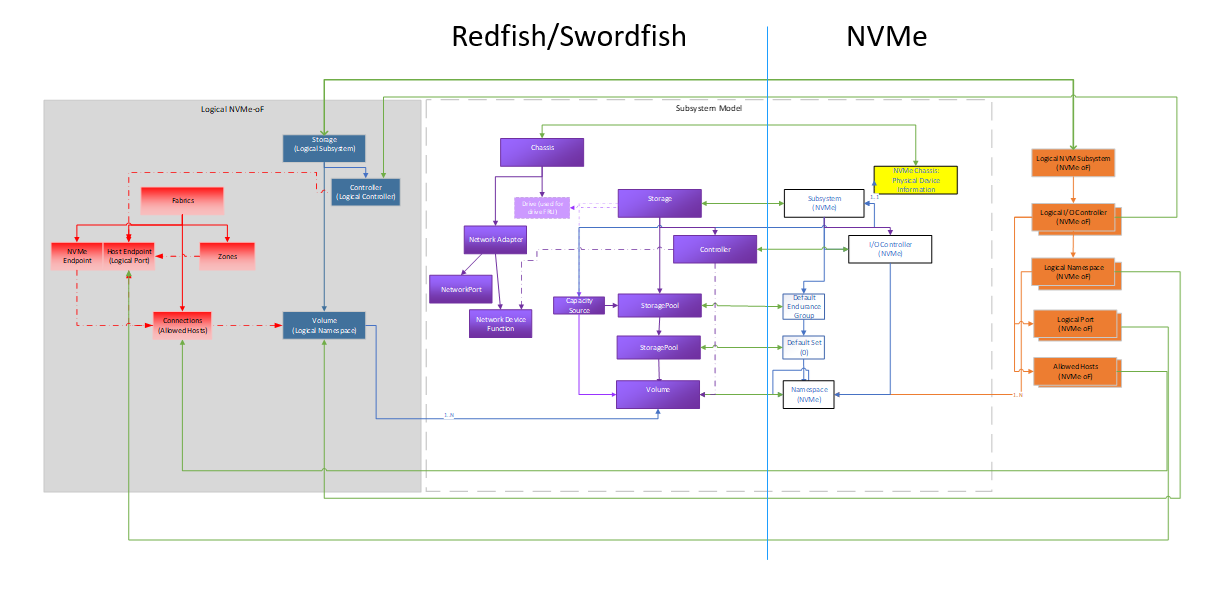
The Figure 2 shows the high level mapping of the key NVMe-oF objects to Redfish / Swordfish schema objects. Following the tenets described in the model overview section, these extend the mapping used in the NVM Subsystem for the logical versions of the objects.
This model also includes the use of the Redfish Fabric model to cover the connectivity aspects of the fabric.
The grey shaded portion of this diagram reflects the logical / exported portion of the NVMe-oF environment represented in Redfish / Swordfish.
This section of the document provides a series of example usages of the model that represent common instantiations of NVMe devices, and how those devices may use the various NVMe, and correspondingly, Redfish and Swordfish objects and schema. This section will not provide comprehensive representations of all potential device types; rather, a representation of several common device types, in order to provide an illustration of the application of the model for those that are unfamiliar with either the NVMe or Redfish / Swordfish ecosystems.
Further, the following sections describe the examples and do not attempt to cover all potential permutations for alternate representations of each device class or possible implementations.
Figure 3 shows a sample representation of a simple NVMe SSD, with a PCIe interface. It is implemented with no endurance group or NVM set functionality; it has only a single namespace capability, and a single IO controller.
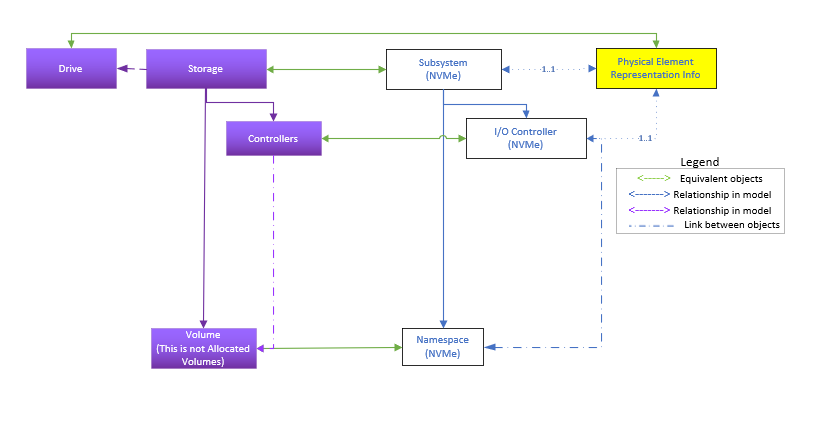
Simple SSDs are SSDs that do not use Endurance Groups or sets. Correspondingly, they only use Storage, Controllers, Volumes (Namespaces), and the Drive schema to represent the fundamental components.
Many SSD implementations support exactly one namespace. These are described by this model, and the mockups reflect this configuration.
This model can also support extensions to cover dual-ported configurations, as well as support for multiple IO controllers per port.
Figure 4 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
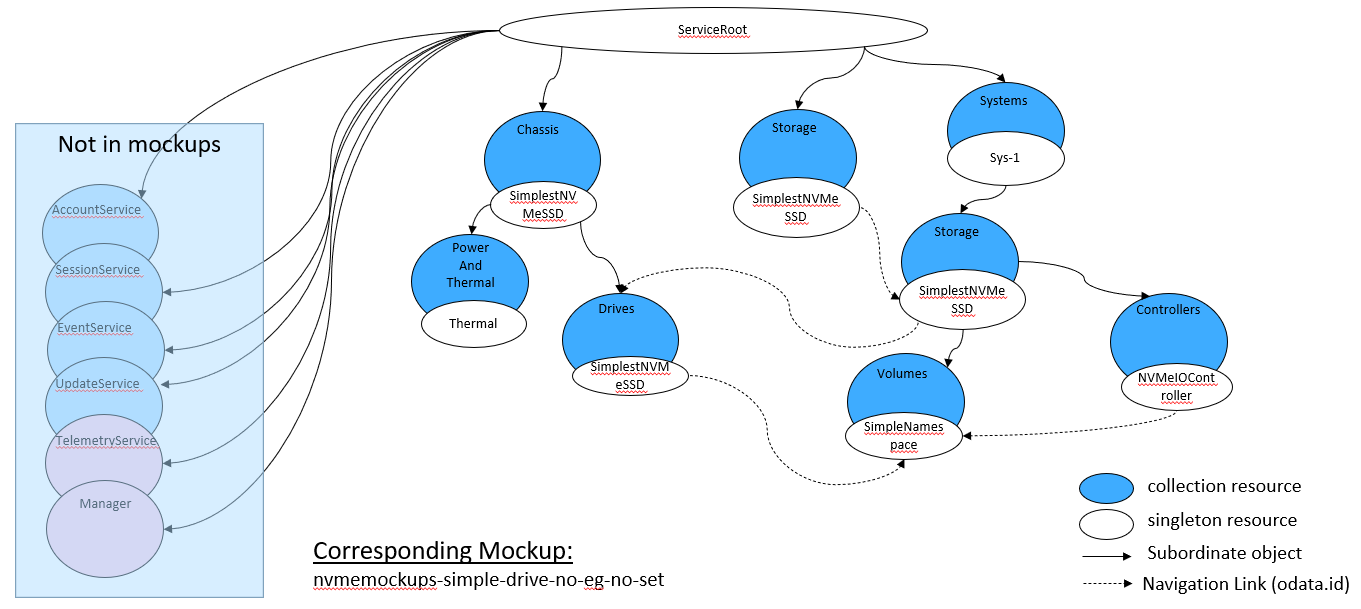
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/simple-ssd-mockups.
Figure 5 shows a sample representation of a complex NVMe SSD, with a PCIe interface. This example shares many similarities to the simple device model, but adds the representation of NVMe Endurance Groups and NVM Sets using the Swordfish StoragePool schema, with additional NVMe specific properties.
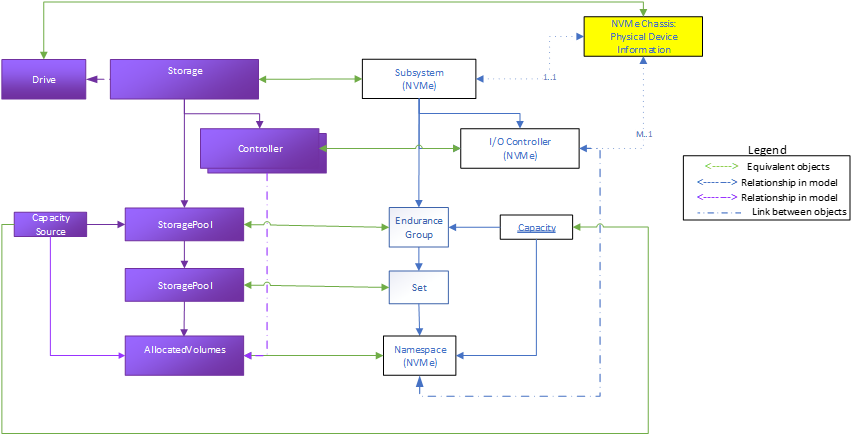
Complex SSDs are SSDs that use Endurance Groups and NVM sets. They also use Storage, Controllers, Volumes (Namespaces), and the Drive schema to represent the fundamental components.
This model can also support extensions to cover dual-ported configurations, as well as support for multiple IO controllers per port.
Endurance Groups divide the media into distinct wear-leveling domains. How this happens is implementation specific.
NVM Sets further subdivide an endurance group in order to limit performance interference within and across these domains.
When this type of device supports dynamic namespace allocation and NVM Sets, the management of the namespaces is done within an NVM Set as the underlying capacity source (e.g., the storage pool).
Figure 6 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/simple-ssd-eg-set-mockups.
This example reflects an IP-attached drive configuration, with a single ethernet port configured, as illustrated in Figure 7. It includes a drive configured with a default endurance group and NVM Set, and is instantiated in the Storage Collection off the Service Root.The network configuration is modeled in the Chassis.
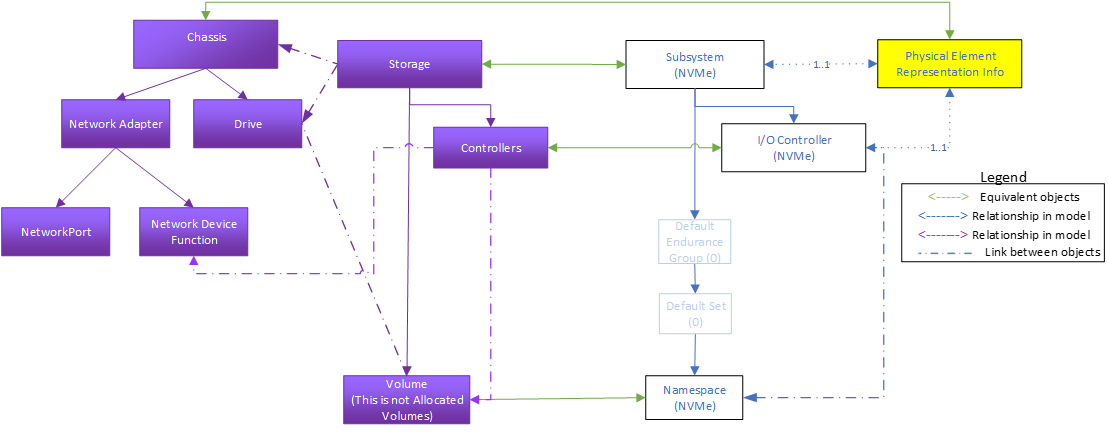
Simple SSDs with IP attach are also SSDs that do not use Endurance Groups or sets, but that have IP-based network interfaces. Correspondingly, they only use Storage, Controllers, Volumes (Namespaces), and the Drive schema to represent the fundamental components. In addition, they use the Redfish Network Adapter, Network Port and Network Device Function to model the configuration of the IP interface port(s).
As with the Simple SSD configuration, Many SSD with IP-attach implementations support exactly one namespace. These are described by this model, and the mockups reflect this configuration.
This model can also support extensions to cover multi-ported configurations, as well as support for multiple IO controllers per port.
Figure 8 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
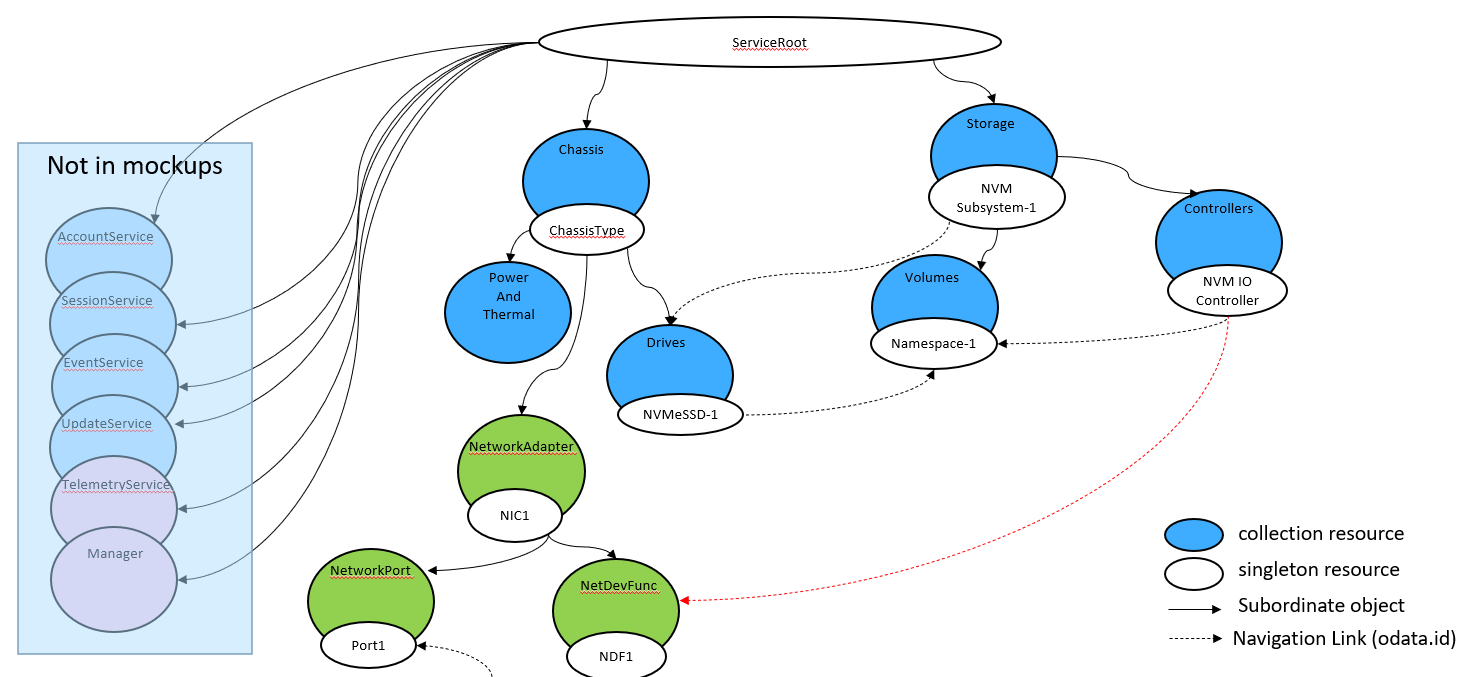
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/ethernet-attach-drive-mockups.
This example covers a representation of a JBOF (“just a bunch of flash”) enclosure and contained drives. This mockup reflects a PCIe front-end attach configuration with a set of drives.
Figure 9 shows only the controller object representation for this JBOF configuration. This includes the admin controller function for enclosure management.
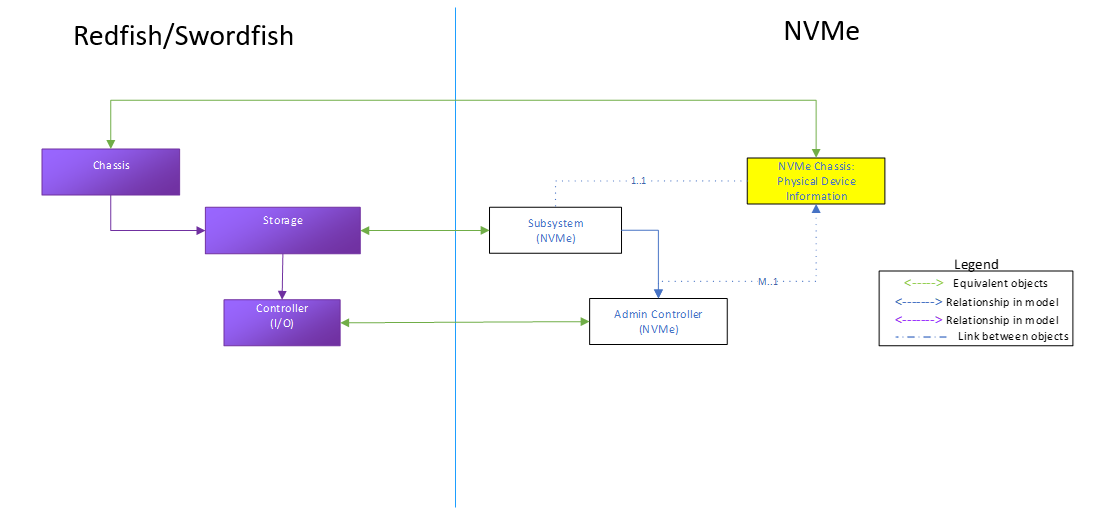
Figure 10 shows the combined object representations for the JBOF system, with both the JBOF controller and NVMe drives (using the Simple SSD style drives) represented in the system. Note that the full mockup represented has 7 drives, while this diagram only represents two for the sake of visual clarity.
This type of JBOF system uses the Chassis, Storage and Controller objects to reflect physical component modeling, Subsystem and Admin Controller functionality.
The Chassis model and Admin controller represent NVM’s SES (SCSI enclosure services) usage.
Figure 11 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/nvme-jbof-mockups.
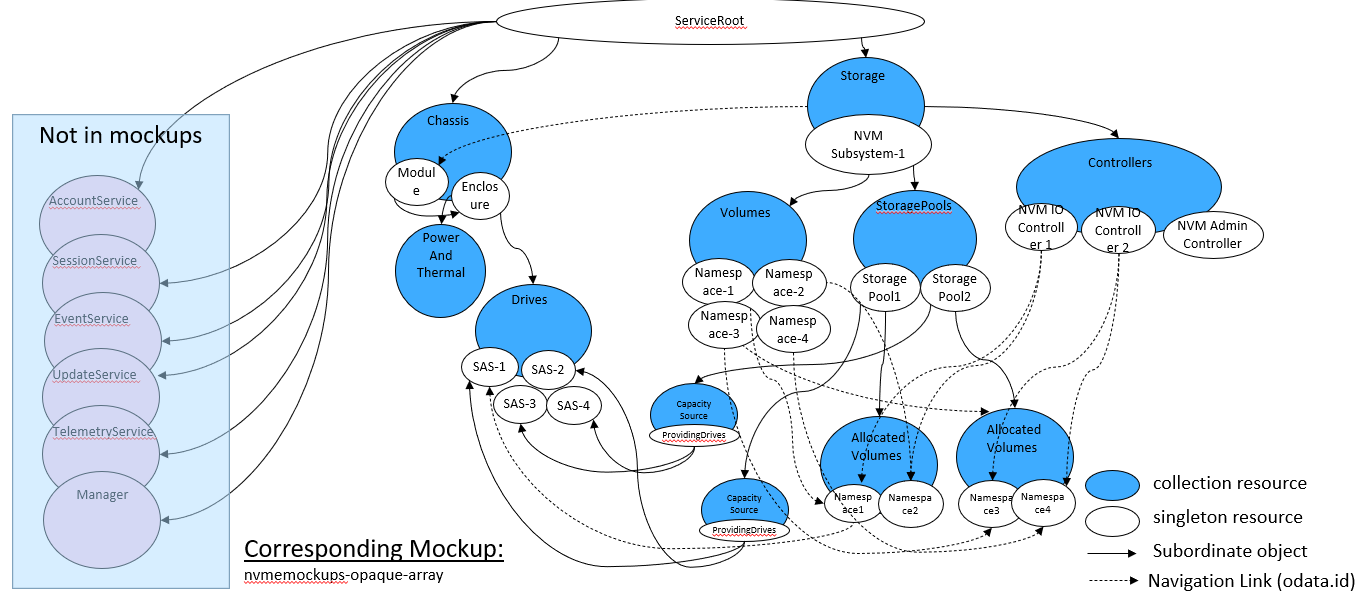
The “opaque” array reflects a system with an NVMe front end, but the internal implementation is vendor specific, and not necessarily presented by the vendor (aka “opaque”). Figure 12 shows a system that presents an NVMe front-end but also exposes a SATA drive backend. This could be done to support both FRU management and volume/namespace creation.
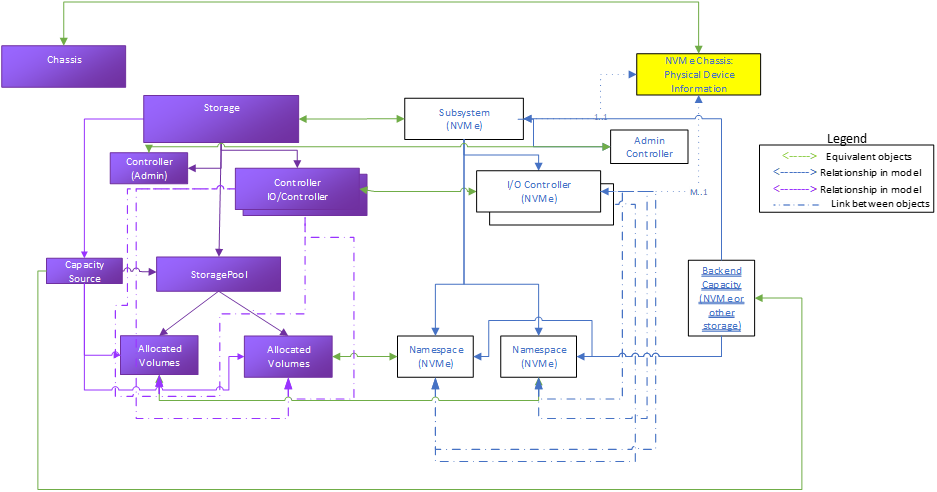
The opaque array example presents NVMe specific information in Redfish/Swordfish objects, using the Storage, Controller, and Volume objects.
In addition, device management information is presented through StoragePool and Drive objects, providing internal, non-NVMe implementation specific information to the user, for configuration, diagnosis and other storage management functions. (This set of objects is subject to the standard Swordfish specification and profiles.)
Figure 13 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
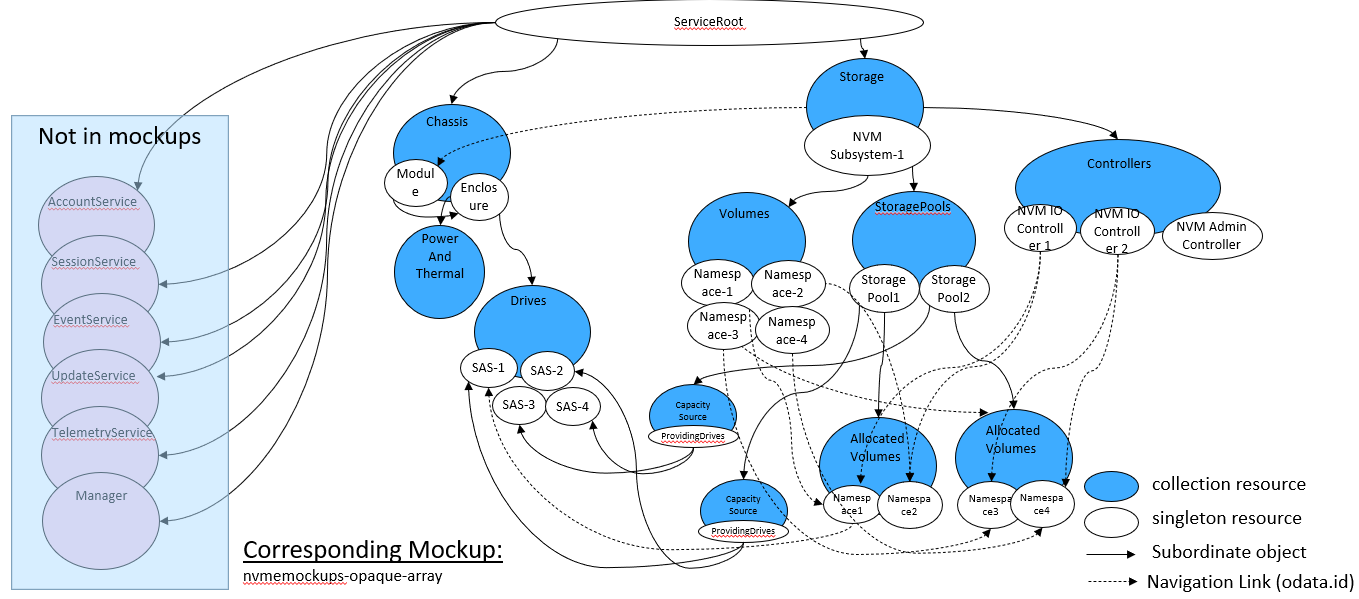
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/nvme-opaque-array-mockups.
Figure 14 shows a logical/exported NVMe-oF subsystem presenting one logical subsystem, one I/O controller, one namespace, one port and representing one allowed host, using the Redfish Fabric model. The fabric model uses the Connection schema to characterize the allowed host information, and Endpoints and Zones to show the network connectivity from the device’s perspective.
This example also includes NVMeDomains. NVMeDomains contain a collection of domain members; these can be NVM controllers, endurance groups, NVM sets, or namespaces.
The fabric attach subsystem example shows the representation of logical, or exported, subsystems, controllers, and namespaces using the Storage, Controller and Volume objects respectively.
It also uses portions of the Redfish fabric model to represent the host attachment information - allowed hosts and logical port - using the Connections and Endpoints objects respectively.
Figure 15 shows the representation, as expressed in the mockup indicated below, of a sample instantiation using Redfish / Swordfish objects.
Note that this mockup does not represent a complete service instantiation; it contains only objects of interest for this context.
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/nvmeof-mockups.
This example describes NVMeDomains. NVMeDomains contain a collection of domain members; these can be NVM controllers, endurance groups, NVM sets, namespaces, and ports, as illustrated in Figure 16.
Domains are used to subdivide an NVM Subsystem. For example, if there are multiple power sources, the domain is used to represent the scope of each power source.
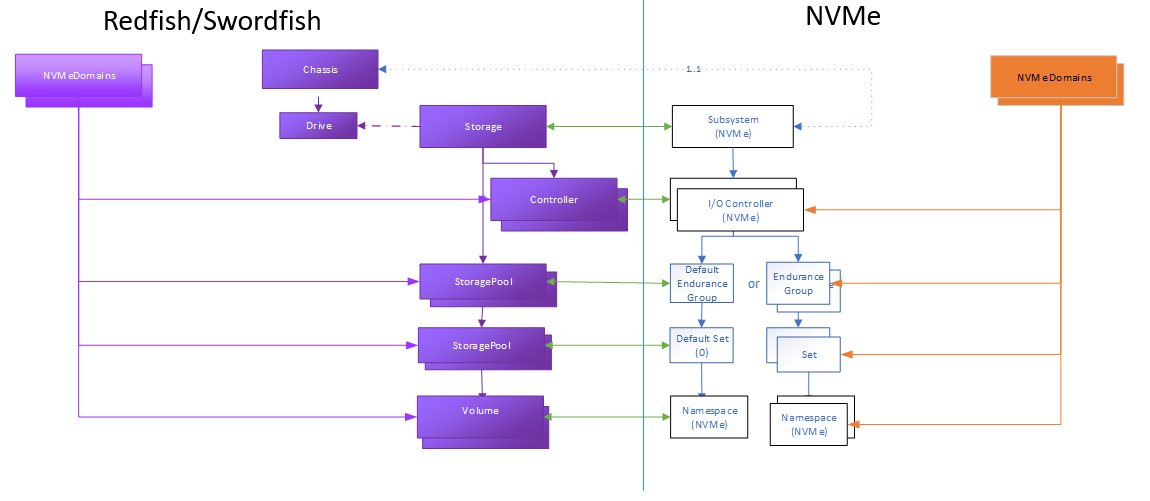
The domain object contains two primary elements: the domain members collection, which contains pointers to the relevant controllers, groups, sets, namespaces, and ports that reflect the appropriate subdivision for the purpose of the domain.
The other primary element includes a set of capacity information properties about this set of domain members.
A corresponding mockup for this configuration can be found at http://swordfishmockups.com/nvmeof-mockups.
The property mapping provided defines the preferred translation between the Redfish/Swordfish schema objects and properties, and the corresponding NVMe and NVMe-oF specification properties. The information is ordered within the Redfish/Swordfish objects; each cross-referenced property within the Redfish/Swordfish structure therefore contains a detailed reference to its mapped property in the NVMe ecosystem.
Each section also includes a sample Redfish/Swordfish mockup presenting an example usage for that object.
Table 4 provides the template and an example for the property mapping provided in the following sections of this document.
For each property (whether a reference, collection, complex type or actual property), there is a comparison between the property in Redfish/Swordfish to the corresponding property in either the NVMe or NVMe-oF specification. The RF/SF property is provided within its schema context; the NVMe/NVMe-oF specification reference is provided within the table, showing both which specification, as well as the section and, if appropriate, the figure in which the property is specified.
Similarly, the type of each property is correspondingly specified. The RF/SF type is specified, and the NVM Spec property type is shown, as well as, where appropriate, any additional identifying information, such as byte offset and data structure.
The Mandatory field is used to specify whether properties are Mandatory or Optional on the NVMe specification side, and in the rare instance where properties are Mandatory in the Redfish/Swordfish schema. (Recommended / required properties for specific implementation types in Redfish/Swordfish will be done separately, through the use of profiles.)
The Notes field can / will be used to include any relevant information about either the purpose of the property, additional context, or other useful information to implementers, such as inter-relationships with other properties.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Redfish / Swordfish Schema Property: RecommendedArbitrationBurstSize |
NVM Spec Property / Field: RecommendedArbitrationBurst(RAB) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2, Figure 249 |
| Type | Redfish / Swordfish Schema Type: String |
NVM Spec Property Type: Power of 2: 2^n Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 72, IdentifyController data structure |
| Description | The Recommended Arbitration Burst Size indicates the maximum number of commands that the controller may launch at one time from a particular Submission Queue. | This is the recommended Arbitration Burst size. The value is in commands and is reported as a power of two (2^n). This is the same units as the Arbitration Burst size. |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the Recommended Arbitration Burst Size indicates the maximum number of commands that the controller may launch at one time from a particular Submission Queue. The value is expressed as a power of two (e.g., 000b indicates one, 011b indicates eight). A value of 111b indicates no limit. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes |
The Redfish/Swordfish Storage schema is used to represent an NVM Subsystem.
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the Storage schema used to represent an NVM Subysystem.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2014-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem",
"@odata.type": "#Storage.v1_9_0.Storage",
"Id": "1",
"Name": "NVMe-oF Logical NVM Fabric System",
"Description": "Mockup of NVMe-oF Logical NVM Fabric System with 1 Logical Subsystem, 1 Logical I/O Controller and 1 Logical port and 1 allowed host.",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK",
"HealthRollup": "OK"
},
"Identifiers": [{
"DurableNameFormat": "NQN",
"DurableName": "nqn.2014-08.org.nvmexpress:uuid:6c5fe566-10e6-4fb6-aad4-8b4159f50245"
}],
"Controllers": {
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Controllers"
},
"Volumes": {
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Volumes/LogicalNamespace1"
}
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 5.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| Type | String | String |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | Uniquely describes the NVM subsystem. |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | The NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name is a UTF-8 null-terminated string used (e.g., by host software) as the unique identifier for the NVM subsystem |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes (see note) |
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Support for this field is mandatory if the controller supports revision 1.2.1 or later as indicated in the Version register (refer to section 3.1.2). Reported in the NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name field of the Identify Controller data structure, bytes 1023:768 (refer to figure 249 in section 5.15.2.1 of the NVMe Base Specification). If the NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name field of the Identify Controller data structure is not supported, then all bytes of this field shall be cleared to 0h. Refer to NVMe Base Specification section 7.9 for the definition of NVMe Qualified Name. Refer to NVMe Base Specifiction section 7.11 for details on the Unique Identifier, including compatibility with older versions of NVMe Controllers that do not support NVM Subsystem NQNs. |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 6.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | N/A |
| Description | The description of this resource. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | N/A |
| Mandatory | No. | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. Implementation may be vendor-unique. | Return the common description: “An NVM subsystem presents a collection of one or more controllers (IO, Admin, and/or Discovery) which are used to access and/or manage namespaces. An NVM subsystem includes one or more controllers, zero or more namespaces, and one or more ports.” |
The mapping for Status.State is summarized in Table 7.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | N/A |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | N/A |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySpare / InTest / Starting / Absent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | There is no simple corresponding property or mappable set of information at this time. Current guidance is do not implement this property. Guidance will be added in a future version of this document as this is an important concept for clients and for consistency with traditional storage devices. |
The mapping for Status.Health is summarized in Table 8.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | Critical Warning Condition |
| Type | Resource.Health | Boolean |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | Indicates the NVM subsystem has detected a condition that causes at least one of bits 0 to 4 in the Critical Warning field of the SMART / Health Information log (refer to NVMe Base Specification section 5.14.1.2) to be set to one. |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | Bits in this field represent the associated state at the time of this event. The Additional Hardware Error Information field shall be set at the time of the event using the same format as is specified for the Critical Warning field of the SMART / Health Information. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | Returned as a Critical Warning Condition (code 06h) in the NVM Subsystem Hardware Error Event data (bytes 01:00) of an NVM Subsystem Hardware Error Event (Event Type 05h) in the Persistent Event Log. Reverence NVMe Base Specification 5.14.1.13.1.5 NVM Subsystem Hardware Error Event (Event Type 05h), Figure 221 and Figure 222. |
The mapping for Status.HealthRollup is summarized in Table 9.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.HealthRollup | Critical Warning |
| Type | Resource.Health | Boolean |
| Description | The overall health state from the view of this resource. | Indicates the NVM subsystem reliability has been degraded due to significant media related errors or any internal error that degrades NVM subsystem reliability. |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource and its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | Indicates if the NVM subsystem reliability has been degraded due to significant media related errors or any internal error that degrades NVM subsystem reliability. Critical warnings regarding the health of the NVM subsystem may be indicated via an asynchronous event notification to the host. The warnings that results in an asynchronous event notification to the host are configured using the Set Features command; refer to section 5.21.1.11. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | Returned in byte 00, bit 1 of the Get Log Page – SMART / Health Information Log. Reference the NVMe Base Specification section 5.14.1.2 - SMART / Health Information (Log Identifier 02h), Figure 196. |
The mapping for Controllers is summarized in Table 10.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Controllers | Controllers |
| Type | StorageControllerCollection. | Controller list. |
| Description | The set of controllers instantiated by this storage subsystem. | A list of controller identifiers in the NVM subsystem that may or may not be attached to namespace(s) |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to a Resource of type StorageControllerCollection that contains the set of storage controllers allocated to this instance of an storage subsystem. | A Controller List (refer to NVMe Bese Specification section 4.11) of up to 2,047 controller identifiers is returned containing a controller identifier greater than or equal to the value specified in the Controller Identifier (CDW10.CNTID) field. The list contains controller identifiers in the NVM subsystem that may or may not be attached to namespace(s). |
| Mandatory | No | No (see note) |
| Notes | This is a collection StorageControllers. Refer to the StorageController schema for details of the instance information. These are used to provide information on NVM IO, Admin and Discovery controllers. | This property is only mandatory for controllers that support the Namespace Management capability - reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.9 Controller list (CNS 13h) |
The mapping for Identifiers is summarized in Table 11.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| Type | Collection(Resource.Identifier) | An array of identifiers |
| Description | The Durable names for the subsystem. | An array of identifiers |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a list of all known durable names for the associated subsystem. | This specifies the NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name as a UTF-8 null-terminated string. Refer to NVMe Base Specification, section 7.9, for the definition of NVMe Qualified Name. Support for this field is mandatory if the controller supports revision 1.2.1 or later as indicated in the Version register (refer to section 3.1.2). |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | This is an array of unique identifiers for the NVM Subsystem. | There will only be one instance in this array for Subsystem. Refer to the Identify Controller data structure (CNS 01h) bits 1023:768 in figure 249 (Identify – Identify Controller Data Structure) of the NVMe Base Specification. |
The mapping for Identifiers.DurableNameFormat is summarized in Table 12.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers.DurableNameFormat | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| Type | Resource.v1_1_0.DurableNameFormat | There is a single value for this array in Subsystem. The property type is of type NVMe Qualified Name (NQN). |
| Description | The format of the Durable names for the subsystem. | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| LongDescription | This specifies the format of the associated NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name of type NQN. Support for this field is mandatory if the controller supports revision 1.2.1 or later as indicated in the Version register (refer to section 3.1.2). | |
| Mandatory | No | Yes |
| Notes | This is an enum with multiple potential values. For this particular usage in Subsystem, there will only be one instance populated, of type NQN. | There will only be one instance in this array for Subsystem. Refer to the Identify Controller data structure (CNS 01h) bits 1023:768 in figure 249 (Identify – Identify Controller Data Structure) of the NVMe Base Specification. |
The mapping for Identifiers.DurableName is summarized in Table 13.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers.DurableName | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| Type | Edm.String | The NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name as a UTF-8 null-terminated string |
| Description | The format of the Durable names for the subsystem. | NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name (SUBNQN) |
| LongDescription | This specifies the NVM Subsystem NVMe Qualified Name as a UTF-8 null-terminated string. Refer to NVMe Base Specification, section 7.9, for the definition of NVMe Qualified Name. Support for this field is mandatory if the controller supports revision 1.2.1 or later as indicated in the Version register (refer to section 3.1.2). | |
| Mandatory | No | Yes |
| Notes | For this particular usage in Subsystem, there will only be one instance populated in the identifiers array. | There will only be one instance in this array for Subsystem. Refer to the Identify Controller data structure (CNS 01h) bits 1023:768 in figure 249 (Identify – Identify Controller Data Structure) of the NVMe Base Specification. |
The mapping for Volumes is summarized in Table 14.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Volumes | Allocated Namespace ID list |
| Type | VolumeCollection.VolumeCollection | List of namespace IDs |
| Description | The set of volumes instantiated by this storage subsystem. | A list of Allocated Namespaces for this Subsystem |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to a Resource of type VolumeCollection that contains the set of storage volumes allocated to this instance of an storage subsystem. | A list of namespace IDs is returned to the host containing allocated NSIDs in increasing order. |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | This is a collection of Namespaces that belong to this NVM Subsystem. Refer to the Volume schema for details of the instance information. | Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.6 Allocated Namespace ID list (CNS 10h). |
The Redfish/Swordfish StorageControllers schema is used to represent an NVM Controller.
There are three different types of NVM Controllers: Admin, Discovery, and IO.
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the StorageController schema used to represent an Admin Controller.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2014-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/OpaqueArray/Controllers/NVMeAdminController",
"@odata.type": "#StorageController.v1_0_0.StorageController",
"Name": "NVMe Admin Controller",
"Description": "Single NVMe Admin Controller for in-band admin command access.",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"Id": "NVMeAdminController",
"Manufacturer": "Best NVMe Vendor",
"Model": "NVMe Connect Array",
"SerialNumber": "NVME123456",
"PartNumber": "NVM44",
"FirmwareVersion": "1.0.0",
"SupportedControllerProtocols": [
"PCIe"
],
"NVMeControllerProperties": {
"ControllerType": "Admin",
"NVMeVersion": "1.3",
"NVMeControllerAttributes": {
"SupportsSQAssociations": false,
"SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive": false,
"SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState": false,
"Supports128BitHostId": false
}
}
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 15.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller ID (CNTLID) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 16-bit hex value Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 79:78, IdentifyController data structure |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | |
| Mandatory | Required | Mandatory |
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the CNTLID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 16.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | |
| Description | The description of this resource. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | |
| Mandatory | Optional | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “An NVM Admin Controller exposes capabilities that allow a host to manage an NVM subsystem. Admin controllers support commands providing management capabilities but does not provide IO access.” |
The mapping for Status.State is summarized in Table 17.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySpare / InTest / Starting / ABsent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | Ready (CSTS.RDY) maps to Enabled, Shutdown (CSTS.SHST) value will tell you if shutdown is in progress or complete (StandbyOffline), ProcessingPaused (CSTS.PP) maps to Deferring. If both Ready and Shutdown are indicated, then the system should indicate StandbyOffline. If both Ready and ProcessingPaused are indicated, then the system should indicate Deferring. |
The mapping for Status.Health is summarized in Table 18.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Resource.Health | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | This comes from CSTS Controller Failure Status, and from the SMART / health information log critical warning field. |
The mapping for SupportControllerProtocols is summarized in Table 19.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | SupportedControllerProtocols | N/A |
| Type | Collection(ProtocolProtocol) | NVM Spec Property Type: N/A |
| Description | The supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This is an array of protocols supported by the StorageController. This can be set to values including, but not limited to, PCIe, RDMA, NVMe-oF, RoCE, RoCEv2, and InfiniBand. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType is summarized in Table 20.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType | N/A |
| Type | StorageController.v1_0_0.NVMeControllerType | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | This property specifies the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This property must be used to specify the type of NVMe Controller. For an admin controller, set to Admin. | Return “Admin” |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion is summarized in Table 21.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion | NVM Spec Property / Field: Version (VER) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: Maps from register 3.1.2. Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 83:90 |
| Description | The version of the NVMe Base Specification supported. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Implementations compliant to revision 1.2 or later of this specification shall report a non-zero value in this field. Map from corresponding value in register 3.1.2 to string as “1.0”, “1.1”, “1.2”, “1.2.1”, “1.3.0”, “1.4.0”, etc. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations is summarized in Table 22.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 8 (SQ Associations) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 8 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports SQ Associations. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports SQ Associations. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.TrafficBasedKeepAlive is summarized in Table 23.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 6 (Traffic Based Keep Alive Support – TBKAS) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 6 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState is summarized in Table 24.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 1 (Non-Operational Power State Permissive Mode) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 1 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId is summarized in Table 25.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 0 NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize is summarized in Table 26.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize | NVM Spec Property / Field: Maximum Queues Entries Supported (MQES) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a; Section 3.1.1 Controller Capabilities; Figure 69 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: Bits 15:00 |
| Description | Indicates the maximum individual queue size that an NVMe IO Controller supports. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the maximum individual queue entry size supported per queue. This is a zero-based value, where the minimum value is one, indicating two entries. For PCIe, this applies to both submission and completion queues. For NVMe-oF, this applies to only submission queues. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics is summarized in Table 27.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics | |
| Type | Collection(StorageController.v1_0_0.ANACharacteristics) | |
| Description | This property contains the combination of ANA type and volume information. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the combination of ANA type and volume information. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded is summarized in Table 28.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSubsystemDegraded | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 2 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the StorageController schema used to represent a Discovery Controller.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2014-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Controllers/NVMeIOController",
"@odata.type": "#StorageController.v1_0_0.StorageController",
"Id": "9",
"Name": "NVMe Logical Discovery Controller",
"Description": "Single NVMe Discovery Controller presented to host.",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"Id": "NVMeDiscoveryController",
"SupportedControllerProtocols": [
"TCP", "RDMA", "FC"
],
"SupportedDeviceProtocols": [
"NVMeOverFabrics"
],
"NVMeControllerProperties": {
"ControllerType": "Discovery",
"NVMeVersion": "1.3",
"NVMeControllerAttributes": {
"SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive": false,
"SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState": false,
"Supports128BitHostId": false
}
}
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 29.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller ID (CNTLID) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 16-bit hex value Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 79:78, IdentifyController data structure |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | |
| Mandatory | Required | Mandatory |
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the CNTLID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 30.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | |
| Description | The description of this resource. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | |
| Mandatory | Optional | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “An NVM Discovery Controller exposes capabilities that allow a host to retrieve information required to connect to one or more NVM Subsystems. Discovery controllers only support commands providing discovery capabilities; they do not provide IO or management access.” |
The mapping for Status.State is summarized in Table 31.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySpare / InTest / Starting / ABsent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | Ready (CSTS.RDY) maps to Enabled, Shutdown (CSTS.SHST) value will tell you if shutdown is in progress or complete (StandbyOffline), ProcessingPaused (CSTS.PP) maps to Deferring. If both Ready and Shutdown are indicated, then the system should indicate StandbyOffline. If both Ready and ProcessingPaused are indicated, then the system should indicate Deferring. |
The mapping for Status.Health is summarized in Table 32.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Resource.Health | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | This comes from CSTS Controller Failure Status, and from the SMART / health information log critical warning field. |
The mapping for SupportControllerProtocols is summarized in Table 33.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | SupportedControllerProtocols | N/A |
| Type | Collection(ProtocolProtocol) | NVM Spec Property Type: N/A |
| Description | The supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This is an array of protocols supported by the StorageController. This can be set to values including, but not limited to, PCIe, RDMA, NVMe-oF, RoCE, RoCEv2, and InfiniBand. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType is summarized in Table 34.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType | N/A |
| Type | StorageController.v1_0_0.NVMeControllerType | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | This property specifies the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This property must be used to specify the type of NVMe Controller. For a discovery controller, set to Discovery. | Return “Discovery” |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion is summarized in Table 35.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion | NVM Spec Property / Field: Version (VER) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: Maps from register 3.1.2. Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 83:90 |
| Description | The version of the NVMe Base Specification supported. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Implementations compliant to revision 1.2 or later of this specification shall report a non-zero value in this field. Map from corresponding value in register 3.1.2 to string as “1.0”, “1.1”, “1.2”, “1.2.1”, “1.3.0”, “1.4.0”, etc. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.TrafficBasedKeepAlive is summarized in Table 36.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 6 (Traffic Based Keep Alive Support – TBKAS) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 6 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState is summarized in Table 37.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 1 (Non-Operational Power State Permissive Mode) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 1 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId is summarized in Table 38.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 0 NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize is summarized in Table 39.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize | NVM Spec Property / Field: Maximum Queues Entries Supported (MQES) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a; Section 3.1.1 Controller Capabilities; Figure 69 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: Bits 15:00 |
| Description | Indicates the maximum individual queue size that an NVMe IO Controller supports. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the maximum individual queue entry size supported per queue. This is a zero-based value, where the minimum value is one, indicating two entries. For PCIe, this applies to both submission and completion queues. For NVMe-oF, this applies to only submission queues. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded is summarized in Table 40.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSubsystemDegraded | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 2 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut is summarized in Table 41.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the available spare capacity has fallen below the threshold. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the available spare capacity has fallen below the threshold. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for Links.AttchedVolumes is summarized in Table 42.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.AttachedVolumes | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Volume.Volume) | N/A |
| Description | An array of links to volumes that are attached to this controller instance. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to the Resources of type Volume that are attached to this instance of storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | Yes | |
| Notes | This contains a pointer to the set of namespaces attached to this IO Controller. |
The mapping for Links.Endpoints is summarized in Table 43.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.Endpoints | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Endpoint.Endpoint) | |
| Description | An array of links to the endpoints that connect to this controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain an array of links to the Resources of type Endpoint associated with this controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for Links.Connections is summarized in Table 44.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.Connections | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Connection.Connection) | |
| Description | An array of links to volumes that are attached to this controller instance. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to the Resources of type Volume that are attached to this instance of storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This contains the information used to represented the allowed hosts. | This property contains pointers to the Connections objects. The information about allowed hosts is mapped to the Connections objects for NVMe-oF configurations. |
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the StorageController schema used to represent an IO Controller.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2014-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Controllers/NVMeIOController",
"@odata.type": "#StorageController.v1_0_0.StorageController",
"Id": "9",
"Name": "NVMe Logical I/O Controller",
"Description": "Single NVMe I/O Controller presented to host.",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"Id": "NVMeIOController",
"SupportedControllerProtocols": [
"TCP", "RDMA", "FC"
],
"SupportedDeviceProtocols": [
"NVMeOverFabrics"
],
"NVMeControllerProperties": {
"NVMeVersion": "1.3",
"NVMeControllerAttributes": {
"ReportsUUIDList": false,
"SupportsSQAssociations": false,
"ReportsNamespaceGranularity": false,
"SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive": false,
"SupportsPredictableLatencyMode": false,
"SupportsEnduranceGroups": false,
"SupportsReadRecoveryLevels": false,
"SupportsNVMSets": false,
"SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState": false,
"Supports128BitHostId": false
},
"ANACharacteristics": [{
"AccessState": "Optimized",
"Volume": {
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Sys-1/Storage/NVMeSSD-EG/Volumes/Namespace1"
}
}]
},
"Links": {
"AttachedVolumes": [{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Sys-1/Storage/NVMeSSD-EG/Volumes/Namespace1"
}],
"Endpoints": [{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Fabrics/NVMe-oF/Endpoints/NVMeEndpoint"
},
{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Fabrics/NVMe-oF/Endpoints/Host"
}
],
"Connections": [{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Fabrics/NVMe-oF/Connections/Host1"
}]
}
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 45.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller ID (CNTLID) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 16-bit hex value Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 79:78, IdentifyController data structure |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | |
| Mandatory | Required | Mandatory |
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the CNTLID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 46.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | |
| Description | The description of this resource. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | |
| Mandatory | Optional | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “An NVM IO controller is a general-purpose controller that provides access to logical block data and metadata stored on an NVM subsystem’s non-volatile storage medium. IO Controllers may also support management capabilities.” |
The mapping for Status.State is summarized in Table 47.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySpare / InTest / Starting / ABsent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | Ready (CSTS.RDY) maps to Enabled, Shutdown (CSTS.SHST) value will tell you if shutdown is in progress or complete (StandbyOffline), ProcessingPaused (CSTS.PP) maps to Deferring. If both Ready and Shutdown are indicated, then the system should indicate StandbyOffline. If both Ready and ProcessingPaused are indicated, then the system should indicate Deferring. |
The mapping for Status.Health is summarized in Table 48.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | NVM Spec Property / Field: CSTS – Controller Status NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 3.1.6, Figure 79 NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Resource.Health | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | This comes from CSTS Controller Failure Status, and from the SMART / health information log critical warning field. |
The mapping for SupportControllerProtocols is summarized in Table 49.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | SupportedControllerProtocols | N/A |
| Type | Collection(ProtocolProtocol) | NVM Spec Property Type: N/A |
| Description | The supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the supported set of protocols for communicating to this storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This is an array of protocols supported by the StorageController. This can be set to values including, but not limited to, PCIe, RDMA, NVMe-oF, RoCE, RoCEv2, and InfiniBand. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType is summarized in Table 50.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ControllerType | N/A |
| Type | StorageController.v1_0_0.NVMeControllerType | NVM Spec Property Type: |
| Description | This property specifies the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This property must be used to specify the type of NVMe Controller. For an IO controller, set to IO. | Return “IO” |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion is summarized in Table 51.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeVersion | NVM Spec Property / Field: Version (VER) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: Maps from register 3.1.2. Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 83:90 |
| Description | The version of the NVMe Base Specification supported. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall specify the type of NVMe Controller. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | Implementations compliant to revision 1.2 or later of this specification shall report a non-zero value in this field. Map from corresponding value in register 3.1.2 to string as “1.0”, “1.1”, “1.2”, “1.2.1”, “1.3.0”, “1.4.0”, etc. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsUUIDList is summarized in Table 52.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsUUIDList | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): UUID List (Bit 9) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 9 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports reporting of a UUID list. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports reporting of a UUID list. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations is summarized in Table 53.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsSQAssociations | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 8 (SQ Associations) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 8 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports SQ Associations. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports SQ Associations. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsNamespaceGranularity is summarized in Table 54.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.ReportsNamespaceGranularity | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 7 (Namespace Granularity) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 7 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports reporting of Namespace Granularity. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports reporting of Namespace Granularity. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.TrafficBasedKeepAlive is summarized in Table 55.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsTrafficBasedKeepAlive | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 6 (Traffic Based Keep Alive Support – TBKAS) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 6 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports restarting KeepAlive Timer if traffic is processed from an admin command or IO during KeepAlive Timeout interval. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.PredictableLatencyMode is summarized in Table 56.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsPredictableLatencyMode | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 5 (Predictable Latency Mode) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 5 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports Predictable Latency Mode. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports Predictable Latency Mode. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.EnduranceGroups is summarized in Table 57.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsEnduranceGroups | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 4 (Endurance Groups) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 4 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports Endurance Groups. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports Endurance Groups. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsReadRecoveryLevels is summarized in Table 58.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsReadRecoveryLevels | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 3 (Read Recovery Levels) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 3 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports Read Recovery Levels. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports Read Recovery Levels. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsNVMSets is summarized in Table 59.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsNVMSets | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 2 (NVM Sets) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 2 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports NVM Sets. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports NVM Sets. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState is summarized in Table 60.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.SupportsExceedingPowerOfNonOperationalState | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 1 (Non-Operational Power State Permissive Mode) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 1 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports exceeding Power of NonOperational State in order to execute controller initiated background operations in a non-operational power state. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId is summarized in Table 61.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeControllerAttributes.Supports128BitHostId | NVM Spec Property / Field: Controller Attributes (CTRATT): Bit 0 NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.2 (IdentifyController), Figure 249 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 99:96 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the controller supports a 128-bit Host Identifier. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize is summarized in Table 62.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.MaxQueueSize | NVM Spec Property / Field: Maximum Queues Entries Supported (MQES) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a; Section 3.1.1 Controller Capabilities; Figure 69 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: Bits 15:00 |
| Description | Indicates the maximum individual queue size that an NVMe IO Controller supports. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the maximum individual queue entry size supported per queue. This is a zero-based value, where the minimum value is one, indicating two entries. For PCIe, this applies to both submission and completion queues. For NVMe-oF, this applies to only submission queues. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics is summarized in Table 63.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics | |
| Type | Collection(StorageController.v1_0_0.ANACharacteristics) | |
| Description | This property contains the combination of ANA type and volume information. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the combination of ANA type and volume information. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.AccessState is summarized in Table 64.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.AccessState | NVM Spec Property / Field: Asymmetric Namespace Access State NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a; Section 5.14.1.12; Figure 211 |
| Type | StorageController.v1_0_0.ANAAccessState | NVM Spec Property Type: Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: Bits 03:00 of Byte 16 |
| Description | Reported ANA Access state. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the reported ANA Access State. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Available values: Optimized / NonOptimized / Inacessible / PersistentLoss |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.Volume is summarized in Table 65.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.ANACharacteristics.Volume | NVM Spec Property / Field: Namespace Identifier X: NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a; Section 5.14.1.12; Figure 211 |
| Type | Volume.Volume | NVM Spec Property Type: Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bits 35:32, 39:36, …, ((n*4) + 35): |
| ((n*4) + 32) - up to “n” namespace identifiers. | ||
| Description | The specified volume. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to the specified volume. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This field contains the pointer to the namespace for which the access state applies. | The namespace id should be redirected / linked to the corresponding namespace (volume) object with that namespace id. If this set of fields contains multiple namespaces (e.g., a group of namespaces), a unique entry in the ANACharacteristics array should be created for each namespace. |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PRMUnreliable is summarized in Table 66.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PMRUnreliable | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 5 of Byte 00 |
| Description | The Persistent Memory Region has become unreliable. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the Persistent Memory Region has become unreliable. PCI Express memory reads may return invalid data or generate poisoned PCI Express TLP(s). Persistent Memory Region memory writes may not update memory or may update memory with undefined data. The Persistent Memory Region may also have become non-persistent. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PowerBackupFailed is summarized in Table 67.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.PowerBackupFailed | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 4 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the volatile memory backup device has failed. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the volatile memory backup device has failed. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.MediaInReadOnly is summarized in Table 68.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.MediaInReadOnly | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 3 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates the media has been placed in read only mode. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate the media has been placed in read only mode. This is not set when the read-only condition on the media is a result of a change in the write protection state of a namespace. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSystemDegraded is summarized in Table 69.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.OverallSubsystemDegraded | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 2 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the NVM subsystem reliability has been compromised. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut is summarized in Table 70.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeControllerProperties.NVMeSMARTCriticalWarnings.SpareCapacityWornOut | NVM Spec Property / Field: Critical Warning NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14.1.2, SMART / Health Information, Figure 196 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 00 |
| Description | Indicates that the available spare capacity has fallen below the threshold. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the available spare capacity has fallen below the threshold. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for Links.AttchedVolumes is summarized in Table 71.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.AttachedVolumes | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Volume.Volume) | N/A |
| Description | An array of links to volumes that are attached to this controller instance. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to the Resources of type Volume that are attached to this instance of storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | Yes | |
| Notes | This contains a pointer to the set of namespaces attached to this IO Controller. |
The mapping for Links.Endpoints is summarized in Table 72.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.Endpoints | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Endpoint.Endpoint) | |
| Description | An array of links to the endpoints that connect to this controller. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain an array of links to the Resources of type Endpoint associated with this controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for Links.Connections is summarized in Table 73.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Links.Connections | N/A |
| Type | Collection(Connection.Connection) | |
| Description | An array of links to volumes that are attached to this controller instance. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a link to the Resources of type Volume that are attached to this instance of storage controller. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This contains the information used to represented the allowed hosts. | This property contains pointers to the Connections objects. The information about allowed hosts is mapped to the Connections objects for NVMe-oF configurations. |
The Redfish/Swordfish Volume schema is used to represent an NVM Namespace.
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the Volume schema used to represent an NVM Namespace.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2014-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Volumes/LogicalNamespace1",
"@odata.type": "#Volume.v1_5_0.Volume",
"Id": "1",
"Name": "Namespace 1",
"LogicalUnitNumber": 1,
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"Identifiers": [{
"DurableNameFormat": "NGUID",
"DurableName": "FEDCBA9876543210h"
}],
"Capacity": {
"Data": {
"ConsumedBytes": 0,
"AllocatedBytes": 10737418240
},
"Metadata": {
"AllocatedBytes": 536870912
}
},
"CapacitySources": [{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/NVMe-oF-Subsystem/Volumes/LogicalNamespace1/CapacitySources/Source1"
}],
"NVMeNamespaceProperties": {
"NamespaceId": "0x014",
"NamespaceFeatures": {
"SupportsThinProvisioning": false,
"SupportsAtomicTransactionSize": false,
"SupportsDeallocatedOrUnwrittenLBError": false,
"SupportsNGUIDReuse": false,
"SupportsIOPerformanceHints": false
},
"NumberLBAFormats": 0,
"FormattedLBASize": "LBAFormat0Support",
"MetadataTransferredAtEndOfDataLBA": false,
"NVMeVersion": "1.4"
}
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 74.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Spec Property / Field: Namespace ID (NSID) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a |
| Type | String | |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | To determine the active NSIDs for a particular controller, the host may follow either of the following methods: 1. Issue an Identify command with the CNS field cleared to 0h for each valid NSID (based on the Number of Namespaces value (i.e., MNAM field or NN field) in the Identify Controller data structure). If a non-zero data structure is returned for a particular NSID, then that is an active NSID; or 2. Issue an Identify command with a CNS field set to 2h to retrieve a list of up to 1,024 active NSIDs. If there are more than 1,024 active NSIDs, continue to issue Identify commands with a CNS field set to 2h until all active NSIDs are retrieved. |
| Mandatory | Yes | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the NSID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 75.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | N/A |
| Description | The description of this resource. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | N/A |
| Mandatory | Yes | N/A |
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “A Namespace is a quantity of non-volatile memory that may be formatted into logical blocks. When formatted, a namespace of size n is a collection of logical blocks with logical block addresses from 0 to (n-1). NVMe systems can support multiple namespaces.” |
The mapping for Status.state is summarized in Table 76.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | Enable (EN) |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | Boolean |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | Indicates if the controller is in ‘enabled’ state. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | When set to ‘1’, then the controller shall process commands based on Submission Queue Tail doorbell writes. When cleared to ‘0’, then the controller shall not process commands nor post completion queue entries to Completion Queues. When this bit transitions from ‘1’ to ‘0’, the controller is reset (i.e., a Controller Reset). That reset deletes all I/O Submission Queues and I/O Completion Queues, resets the Admin Submission Queue and Completion Queue, and brings the hardware to an idle state. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySare / InTest / Starting / Absent / UnavailableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | Reference Controller Configuration (CC), offset 14h, bit 00 of the NVMe Base Specification (figure 78) |
The mapping for Status.Health is summarized in Table 77.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | Controller Fatal Status (CSTS.CFS) |
| Type | Resource.Health | Bit |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | Indicates if the controller is able to communicate with host software via completion queue entries in the Admin Completion Queue or I/O Completion Queues. |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | If the controller has a serious error condition and is unable to communicate with host software via completion queue entries in the Admin Completion Queue or I/O Completion Queues, then the controller may set the Controller Fatal Status (CSTS.CFS) bit to ‘1’ (refer to section 3.1.6). This indicates to host software that a serious error condition has occurred. When this condition occurs, host software should attempt to reset and then re-initialize the controller. The Controller Fatal Status condition is not indicated with an interrupt. If host software experiences timeout conditions and/or repeated errors, then host software should consult the Controller Fatal Status (CSTS.CFS) bit to determine if a more serious error has occurred. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | Reference Figure 222 (NVM Subsystem Hardware Error Event Codes) bit 09h of the NVMe Base Specification. |
The mapping for Status.HealthRollup is summarized in Table 78.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.HealthRollup | N/A |
| Type | Resource.Health | N/A |
| Description | The overall health state from the view of this resource. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource and its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | N/A |
| Mandatory | No | N/A |
| Notes | Do not use for Namespace. There are no dependent resources. | Do not implement. |
The mapping for LogicalUnitNumber is summarized in Table 79.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | LogicalUnitNumber | N/A |
| Type | Int64 | N/A |
| Description | Indicates the host-visible LogicalUnitNumber assigned to this Volume. | N/A |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain host-visible LogicalUnitNumber assigned to this Volume. This property shall only be used when in a single connect configuration and no StorageGroup configuration is used. | N/A |
| Mandatory | No | N/A |
| Notes | Do not use with NVMe devices. This is represented more correctly with NamespaceId. | Do not implement. |
The mapping for Identifiers is summarized in Table 80.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers | Namespace Identification Descriptor list |
| Type | Collection(Resource.Identifier) | A variable length Namespace Identification Descriptor structures |
| Description | The Durable names for the storage controller. | A list of Namespace Identification Descriptor structures containing Namespace Type, Namespace Identifier Length (NIDL), and Namespace ID (NID). |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a list of all known durable names for the associated storage controller. | A list of any number of variable length Namespace Identification Descriptor structures that fit into the 4,096 byte Identify payload. All remaining bytes after the namespace identification descriptor structures should be cleared to 0h, and the host shall interpret a Namespace Identifier Descriptor Length (NIDL) value of 0h as the end of the list. The host should ignore any Namespace Identification Descriptor with a Namespace Identifier Type not supported by the host. |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | This is an array of unique identifiers for the NVM Subsystem including Namespace Type and Namespace ID. | Refer to NVMe Base Specification Figure 246 CNS 03h and Figure 251 (Identify – Namespace Identification Descriptor). |
The mapping for Identifiers.DurableName is summarized in Table 81.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers.DurableName | Namespace Identifier (NID) |
| Type | Variable - see notes | Variable - see notes |
| Description | The Durable names for the storage controller. | Durable Namespace Identifier |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a list of all known durable names for the Namespace. | A list of globally unique values assigned to the Namespace when the Namespace is created. Values remain fixed throughout the life of the Namespace and are preserved across Namespace and Controller operations (e.g., Controller Level Reset, Namespace format, etc.). |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | This is an array of unique identifiers for the Namespace. Type and length of descriptor are in the corresponding Identifiers.DurableNameFormat property. | This is an array of unique identifiers for the NVM Namespace. Type and length of the descriptor are in the corresponding Namespace Identifier Type (NIDT). Refer to NVMe Base Specification Figure 246 CNS 03h and Figure 251 - Figure 251 Byte NID of Identify – Namespace Identification Descriptor. |
The mapping for Identifiers.DurableNameFormat is summarized in Table 82.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Identifiers.DurableNameFormat | Namespace Identifier Type (NIDT) |
| Type | Int64 | Int64 |
| Description | The Durable names for the storage controller. | The Namespace Identifier data type and length. |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a list of the types for all known durable names for the associated storage controller. The type determines the length of the corresponding Namespace ID | the data type contained in the Namespace Identifier field and the length of that type as defined in the NVMe Base Specification Figure 251 - Identify (Namespace Identification Descriptor) byte 00. Allowed values are: 1 = an 8-byte IEEE Extended Unique Identifier . 2 = a 10-byte Namespace Globally Unique Identifier. 3 = an 8-byte Namespace UUID |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | This is an array of types for the unique identifiers for the NVM Subsystem. Values may be ‘EUI64’, ‘NGUID’, or ‘UUID’. | Refer to NVMe Base Specification Figure 246 CNS 03h and Figure 251 - Figure 251 (NIDT) of Identify – Namespace Identification Descriptor. |
The mapping for Capacity.Data.ConsumedBytes is summarized in Table 83.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.ConsumedBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: Namespace Utilization (NUSE) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: int 64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 23:16, Identify Namespace data structure |
| Description | The number of bytes consumed in this data store for this data type. | The current number of logical blocks allocated in the namespace. |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of logical bytes currently consumed in this data store for this data type. | This field indicates the current number of logical blocks allocated in the namespace. This field is smaller than or equal to the Namespace Capacity. The number of logical blocks is based on the formatted LBA size. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Reporting capacity in bytes is the Redfish and Swordfish standard mechanism. Clients expect the capacity information to be reported consistently for these devices, so the calculation here is to convert the NVMe properties (in blocks) to bytes. | Returned in bytes 23:16 of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (NVM Command Set Specific). Reference NVMe Base Specification section n 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for Capacity.Data.ProvisionedBytes is summarized in Table 84.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.ProvisionedBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: NVM Capacity (NCAP) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: int 64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 15:08, Identify Namespace data structure |
| Description | The maximum number of bytes that can be allocated in this data store for this data type. | The total size of the namespace in logical blocks (LBA 0 through n-1). |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the maximum number of bytes that can be allocated in this data store for this data type. | This field indicates the total size of the namespace in logical bytes. The value is in bytes. A namespace of size n consists of LBA 0 through (n - 1). The number of logical blocks is based on the formatted LBA size. This field is undefined prior to the namespace being formatted. |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | This property is required when issuing a create namespace command. It is also required for “change namespace” when modifying the size of the namespace. | Returned in bytes 07:00 of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (NVM Command Set Specific). Reference NVMe Base Specification section in 5.15.2.1 and figure 247. |
The mapping for Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes is summarized in Table 85.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: Namespace Size (NSZE) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: int 64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 07:00, Identify Namespace data structure |
| Description | The number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | The total size of the NVM allocated to this namespace. |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | The total size of the NVM allocated to this namespace. The value is in bytes. This field shall be supported if the Namespace Management capability (refer to NVMe Base Specification section 8.12) is supported. This field may not correspond to the logical block size multiplied by the Namespace Size field. Due to thin provisioning or other settings (e.g., endurance), this field may be larger or smaller than the Namespace Size reported. |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | Reporting capacity in bytes is the Redfish and Swordfish standard mechanism. | Returned in bytes 63:48 of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (NVM Command Set Specific). Reference NVMe Base Specification section in 5.15.2.1 and figure 247. |
The mapping for Capacity.Metadata is summarized in Table 86.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Metadata.* | N/A |
| Type | Int64 | N/A |
| Description | The number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | N/A |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | N/A |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | Do not return metadata information for NVMe devices. This is included in the overall reported capacity information. |
The mapping for CapacitySources is summarized in Table 87.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | CapacitySources | NVM Spec Property / Field: NVM Set Identifier (NVMSETID) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Collection(Capacity.CapacitySource) | NVM Spec Property Type: int 64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 101:100, Identify Namespace data structure |
| Description | An array of space allocations to this volume. | The NVM Set in which the namespace is allocated |
| LongDescription | Fully or partially consumed storage from a source resource. Each entry provides capacity allocation information from a named source resource. | |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | Contains the information about the entity providing capacity (e.g, EnduranceGroup) for this namespace. This property is a collection pointer; each CapacitySource instance contains a CapacitySource object. The CapacitySource contains the overall capacity (in bytes), the types and pointers to the underlying capacity sources. |
For NVMe devices that do not implement Endurance Groups and NVM Sets, it is recommended that the CapacitySource not be implemented. For Implementations that do instantiate Endurance Groups and NVM Sets, the capacity source should be implemented as a pointer to the corresponding Endurance Group. (See mockups for examples.) |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceId is summarized in Table 88.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceId | Namespace Identifier (NSID) |
| Type | String | 8-byte value |
| Description | The NVMe Namespace Identifier for this namespace. | An identifier used by a controller to provide access to a namespace. |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the NVMe Namespace Identifier for this namespace. This property shall be a hex value. Namespace identifiers are not durable and do not have meaning outside the scope of the NVMe subsystem. NSID 0x0, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFE are special purpose values. |
An identifier used by a controller to provide access to a namespace or the name of the field in the SQE that contains the namespace identifier. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | To determine the active NSIDs for a particular controller, the host may follow either of the following methods: 1. Issue an Identify command with the CNS field cleared to 0h for each valid NSID (based on the Number of Namespaces value (i.e., MNAM field or NN field) in the Identify Controller data structure). If a non-zero data structure is returned for a particular NSID, then that is an active NSID; or 2. Issue an Identify command with a CNS field set to 2h to retrieve a list of up to 1,024 active NSIDs. If there are more than 1,024 active NSIDs, continue to issue Identify commands with a CNS field set to 2h until all active NSIDs are retrieved. |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.IsShareable is summarized in Table 89.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.IsShareable | NVM Spec Property / Field: Namespace Multi-path I/O and Namespace Sharing Capabilities (NMIC) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 30 |
| Description | Indicates the namespace is shareable. | Specifies multi-path I/O and namespace sharing capabilities of the namespace. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether the namespace is shareable. | If set to ‘1’, then the namespace may be attached to two or more controllers in the NVM subsystem concurrently (i.e., may be a shared namespace). Bits 7:1 are reserved. Bit 0, if cleared to ‘0’, indicates the namespace is a private namespace and is able to be attached to only one controller at a time. |
| Mandatory | No | No |
| Notes | Returned in byte 30 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsThinProvisioning is summarized in Table 90.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsThinProvisioning | NVM Spec Property / Field: THINP NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 0 of Byte 24 |
| Description | This property indicates whether or not the NVMe Namespace supports thin provisioning. | Indicates that the namespace supports thin provisioning |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the NVMe Namespace supports thin provisioning. Specifically, the namespace capacity reported may be less than the namespace size. | if set to ‘1’ indicates that the namespace supports thin provisioning. If cleared to ‘0’ indicates that thin provisioning is not supported. Refer to NVMe Base Specification section 6.1.7 for details on the usage of this field. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 24, bit 0 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsDeallocatedOrUnwrittenLBError is summarized in Table 91.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsDeallocatedOrUnwrittenLBError | NVM Spec Property / Field: DAE NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 2 of Byte 24 |
| Description | This property indicates that the controller supports deallocated or unwritten logical block error for this namespace. | Indicates that the controller supports the Deallocated or Unwritten Logical Block error for this namespace. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the controller supports deallocated or unwritten logical block error for this namespace. | If set to ‘1’ indicates that the controller supports the Deallocated or Unwritten Logical Block error for this namespace. If cleared to ‘0’, then the controller does not support the Deallocated or Unwritten Logical Block error for this namespace. Refer to NVMe Base Specification section 6.7.1.1 |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 24, bit 2 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247. |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsNGUIDReuse is summarized in Table 92.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsNGUIDReuse | NVM Spec Property / Field: UIDREUSE NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 3 of Byte 24 |
| Description | This property indicates that the namespace supports the use of an NGUID (namespace globally unique identifier) value. | Indicates if the value in the NGUID field and the value in the EUI64 field for this namespace may be reused by the controller for a new namespace created after this namespace is deleted. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the namespace supports the use of an NGUID (namespace globally unique identifier) value. | If set to ‘1’ indicates that the value in the NGUID field for this namespace, if non-zero, is never reused by the controller and that the value in the EUI64 field for this namespace, if non-zero, is never reused by the controller. If cleared to ‘0’, then the NGUID value may be reused and the EUI64 value may be reused by the controller for a n3333ew namespace created after this namespace is deleted. This bit shall be cleared to ‘0’ if both NGUID and EUI64 fields are cleared to 0h. Refer to NVMe Base Specification, section 7.11. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 24, bit 3 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsAtomicTransactionSize is summarized in Table 93.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsAtomicTransactionSize | NVM Spec Property / Field: OPTPERF NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 4 of Byte 24 |
| Description | Indicates whether or not the NVM fields for Namespace preferred write granularity (NPWG), write alignment (NPWA), deallocate granularity (NPDG), deallocate alignment (NPDA) and optimimal write size (NOWS) are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for I/O optimization. | Indicates support for the fields NPWG, NPWA, NPDG, NPDA, and NOWS for this namespace; and optimal Write Size field in NVM Sets Attributes Entry |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the NVM fields for Namespace preferred write granularity (NPWG), write alignment (NPWA), deallocate granularity (NPDG), deallocate alignment (NPDA) and optimimal write size (NOWS) are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for I/O optimization. | If set to ‘1’ indicates that the fields NAWUN, NAWUPF, and NACWU are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for this namespace instead of the AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU fields in the Identify Controller data structure. If cleared to ‘0’, then the controller does not support the fields NAWUN, NAWUPF, and NACWU for this namespace. In this case, the host should use the AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU fields defined in the Identify Controller data structure in Figure 247. Refer to NVMe Base Specification section 6.4. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 24, bit 4 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsIOPerformanceHints is summarized in Table 94.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NamespaceFeatures.SupportsIOPerformanceHints | NVM Spec Property / Field: NSABP NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | NVM Spec Property Type: Single bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 1 of Byte 24 |
| Description | Indicates that the Namepsace Atomic Write Unit Normal (NAWUN), Namespace Atomic Write Unit Power Fail (NAWUPF), and Namespace Atomic Compare and Write Unit (NACWU) fields are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for this namespace instead of the controller-level properties AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU. | indicates whether or not the fields NAWUN, NAWUPF, and NACWU are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for this namespace instead of the AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU fields in the Identify Controller data structure. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate that the Namepsace Atomic Write Unit Normal (NAWUN), Namespace Atomic Write Unit Power Fail (NAWUPF), and Namespace Atomic Compare and Write Unit (NACWU) fields are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for this namespace instead of the controller-level properties AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU. | If set to ‘1’ indicates that the fields NAWUN, NAWUPF, and NACWU are defined for this namespace and should be used by the host for this namespace instead of the AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU fields in the Identify Controller data structure. If cleared to ‘0’, then the controller does not support the fields NAWUN, NAWUPF, and NACWU for this namespace. In this case, the host should use the AWUN, AWUPF, and ACWU fields defined in the Identify Controller data structure in NVMe Base Specification Figure 247. Refer to NVMe Base Specification section 6.4. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 24, bit 1 of the Namespace Features (NSFEAT) of the of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247). |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NumberLBAFormats is summarized in Table 95.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NumberLBAFormats | NVM Spec Property / Field: Number of LBA Formats (NLBAF) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Int64 | Type:** Int64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 25 |
| Description | The number of LBA data size and metadata size combinations supported by this namespace. The value of this property is between 0 and 16. | The number of supported LBA data size and metadata size combinations supported by the namespace. |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the number of LBA data size and metadata size combinations supported by this namespace. The value of this property is between 0 and 16. LBA formats with an index set beyond this value will not be supported. | This property shall contain the number of LBA formats allocated in order starting with 0 and packed sequentially. This is a 0’s based value. The maximum number of LBA formats that may be indicated as supported is 16. The supported LBA formats are indicated in bytes 128 to 191 in this data structure. The LBA Format fields with an index beyond the value set in this field are invalid and not supported. LBA Formats that are valid, but not currently available may be indicated by setting the LBA Data Size for that LBA Format to 0h. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 25 (Number of LBA Formats) of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 & figure 247. |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.FormattedLBASize is summarized in Table 96.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.FormattedLBASize | NVM Spec Property / Field: Formatted LBA Size (FLBAS) NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Int64 | Type:** Int64 Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 26 |
| Description | The LBA data size and metadata size combination that the namespace has been formatted with. | The LBA data size and metadata size combination that the namespace has been formatted with. |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the LBA data size and metadata size combination that the namespace has been formatted with. This is a 4-bit data structure. | This field indicates the LBA data size & metadata size combination that the namespace has been formatted with (refer to section 5.23). Bits 3:0 indicates one of the 16 supported LBA Formats indicated in this data structure. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 26 (Formatted LBA Size), bits 3:0 of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247. |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.MetadataTransferredAtEndOfDataLBA is summarized in Table 97.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.MetadataTransferredAtEndOfDataLBA | NVM Spec Property / Field: Metadata transferred at end of LBA NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.1 (Identify Namespace), Figure 247 |
| Type | Boolean | Type:** Bit (bool) Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: Bit 4 of Byte 26 |
| Description | This property indicates whether or not the metadata is transferred at the end of the LBA creating an extended data LBA. | This property indicates whether or not the metadata is transferred at the end of the data LBA. |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether or not the metadata is transferred at the end of the LBA creating an extended data LBA. | If set to ‘1’ indicates that metadata is transferred at the end of the data LBA, creating an extended data LBA. Bit 4 if cleared to ‘0’ indicates that all of the metadata for a command is transferred as a separate contiguous buffer of data. |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in byte 26 (Formatted LBA Size), bit 4 of the Identify Namespace Data Structure (Reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.1 and figure 247. Bit 4 is not applicable when there is no metadata. |
The mapping for NVMeNamespaceProperties.NVMeVersion is summarized in Table 98.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeNamespaceProperties.NVMeVersion | Version (VER) |
| Type | String | Int64 |
| Description | The version of the NVMe Base Specification supported. | This property shall contain the version of the NVMe Base Specification supported. |
| LongDescription | Indicates the major, minor, and tertiary version of the NVM Express base specification that the controller implementation supports. Valid versions of the specification are: 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.2.1, 1.3, and 1.4. | |
| Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
| Notes | Returned in bytes 83:80 of the Identify Controller data structure - CNS 01h (reference NVMe Base Specification section 5.15.2.2 and figure 249. |
The Redfish/Swordfish Storage Pool schema is used to represent an NVM Endurance Group.
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the Storage Pool schema used to represent an NVM Endurance Group.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2015-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/FabricAttachArray/StoragePools/EnduranceGroup1",
"@odata.type": "#StoragePool.v1_4_0.StoragePool",
"Id": "1",
"Name": "Endurance Group 1",
"Description": "Single Endurance Group",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties": {
"EndGrpLifetime": {
"PercentUsed": 0,
"EnduranceEstimate": 0,
"DataUnitsRead": 0,
"DataUnitsWritten": 0,
"MediaUnitsWritten": 0,
"HostReadCommandCount": 0,
"HostWriteCommandCount": 0,
"MediaAndDataIntegrityErrorCount": 0,
"ErrorInformationLogEntryCount": 0
}
},
"Capacity": {
"Data": {
"AllocatedBytes": 10995116277760,
"ConsumedBytes": 10995116277760
}
},
"CapacitySources": [{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/FabricAttachArray/StoragePools/EnduranceGroup1/CapacitySources/Source1"
}]
}The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 99.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | Endurance Group ID NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.14,1,9, Get Log Page - Endurance Group Log |
| Type | String | 16-bit value |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the Endurance Group ID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
The mapping for Description is summarized in Table 100.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | N/A |
| Type | String | N/A |
| Description | The description of this resource. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “An Endurance Group consists of zero or more NVM Sets. Endurance Groups divide the media into distinct wear-leveling domains.” |
The mapping for Status.State is summarized in Table 101.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | N/A |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | N/A |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | Do not implement | |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySare / InTest / Starting / ABsent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | There is not a clear mapping for State of an Endurance Group. Do not implement this property. |
The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 102.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | N/A |
| Type | Resource.Health | N/A |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | |
| Mandatory | Do not implement | |
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | There is not a clear mapping for health of an Endurance Group. Do not implement this property. |
The mapping for Name is summarized in Table 103.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.ConsumedBytes | The Consumed (allocated to NVM Sets) Endurance Group Capacity. Just the “Total Endurance Group Capacity” (TEGCAP) minus the Uallocated Endurance Group Capacity (UEGCAP) in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 + TP 4009 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | The number of bytes consumed in this data store for this data type. | |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of logical bytes currently consumed in this data store for this data type. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Note: This is not in 1.4a because TP 4009 was not integrated. |
The mapping for Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes is summarized in Table 104.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes | The Total Endurance Group Capacity. Just the “Total Endurance Group Capacity” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 + TP 4009 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | The number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Note: This is not in 1.4a because TP 4009 was not integrated. |
The mapping for CapacitySources is summarized in Table 105.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | CapacitySources | |
| Type | Collection(Capacity.CapacitySource) | |
| Description | An array of space allocations to this volume. | |
| LongDescription | Fully or partially consumed storage from a source resource. Each entry provides capacity allocation information from a named source resource. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Contains the information about the providing capacity (e.g, EnduranceGroup) for this namespace. | Do not implement. |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.PredictedMediaLifeLeftPercent is summarized in Table 106.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.PredictedMediaLifeLeftPercent | “Percentage Used” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Decimal % | |
| Description | The percentage of reads and writes that are predicted to be available for the media. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain an indicator of the percentage of life remaining in the drive’s media. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Inverse of “Percentage Used” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 . Subtract the percentage used from 100% to report this value. |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.PercentUsed is summarized in Table 107.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.PercentUsed | “Percentage Used” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | A vendor-specific estimate of the percent life used for the endurance group based on the actual usage and the manufacturer prediction of NVM life. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain A vendor-specific estimate of the percent life used for the endurance group based on the actual usage and the manufacturer prediction of NVM life. A value of 100 indicates that the estimated endurance of the NVM in the Endurance Group has been consumed, but may not indicate an NVM failure. According to the NVMe and JEDEC specs, the value is allowed to exceed 100. Percentages greater than 254 shall be represented as 255. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.EnduranceEstimate is summarized in Table 108.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.EnduranceEstimate | “Endurance Estimate” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | This property contains an estimate of the total number of data bytes that may be written to the Endurance Group over the lifetime of the Endurance Group assuming a write amplication of 1. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain an estimate of the total number of data bytes that may be written to the Endurance Group over the lifetime of the Endurance Group assuming a write amplication of 1. The value is reported in billions, where a value of 1 corresponds to 1 billion bytes written, and is rounded up. A value of zero indicates endurance estimates are unsupported. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsRead is summarized in Table 109.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsRead | |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | The property contains the total number of data units read from this endurance group. | |
| LongDescription | The property shall contain the total number of data units read from this endurance group. This value does not include controller reads due to internal operations such as garbage collection. The value is reported in billions, where a value of 1 corresponds to 1 billion bytes written, and is rounded up. A value of zero indicates the property is unsupported. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsWritten is summarized in Table 110.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.DataUnitsWritten | “Data Units Written” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | The property contains the total number of data units written from this endurance group. | |
| LongDescription | The property shall contain the total number of data units written from this endurance group. This value does not include controller writes due to internal operations such as garbage collection. The value is reported in billions, where a value of 1 corresponds to 1 billion bytes written, and is rounded up. A value of zero indicates the property is unsupported. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaUnitsWritten is summarized in Table 111.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaUnitsWritten | “Media Units Written” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | The property contains the total number of data units written from this endurance group. | |
| LongDescription | The property shall contain the total number of data units written from this endurance group. This value includes host and controller writes due to internal operations such as garbage collection. The value is reported in billions, where a value of 1 corresponds to 1 billion bytes written, and is rounded up. A value of zero indicates the property is unsupported. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostReadCommandCount is summarized in Table 112.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostReadCommandCount | “Host Read Commands” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | This property contains the number of read commands completed by all controllers in the NVM subsystem for the Endurance Group. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the number of read commands completed by all controllers in the NVM subsystem for the Endurance Group. For the NVM command set, the is the number of compare commands and read commands. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostWriteCommandCount is summarized in Table 113.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.HostWriteCommandCount | “Host Write Commands” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | This property contains the number of write commands completed by all controllers in the NVM subsystem for the Endurance Group. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the number of write commands completed by all controllers in the NVM subsystem for the Endurance Group. For the NVM command set, the is the number of compare commands and write commands. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaAndDataIntegrityErrorCount is summarized in Table 114.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.MediaAndDataIntegrityErrorCount | “Media and Data Integrity Errors” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | This property contains the number of occurences where the controller detected an unrecovered data integrity error for the Endurance Group. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the number of occurences where the controller detected an unrecovered data integrity error for the Endurance Group. Errors such as uncorrectable ECC, CRC checksum failure, or LBA tag mismatch are included in this field. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The mapping for NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.ErrorInformationLogEntryCount is summarized in Table 115.
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeEnduranceGroupProperties.EndGrpLifetime.ErrorInformationLogEntryCount | “Number of Error Information Log Entries” in the Endurance Group Log. See 5.14.1.9 |
| Type | Int64 | |
| Description | This property contains the number of error information log entries over the life of the controller for the endurance group. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the number of error information log entries over the life of the controller for the endurance group. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
The Redfish/Swordfish Storage Pool schema is used to represent an NVM Set.
The following mockup shows a sample representation of the Storage Pool schema used to represent an NVM Set.
{
"@Redfish.Copyright": "Copyright 2015-2020 SNIA. All rights reserved.",
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/FabricAttachArray/StoragePools/NVMeSet1",
"@odata.type": "#StoragePool.v1_4_0.StoragePool",
"Id": "1",
"Name": "Set 1",
"Description": "First Set",
"Status": {
"State": "Enabled",
"Health": "OK"
},
"NVMeSetProperties": {
"SetIdentifier": "0x1F",
"EnduranceGroupIdentifier": "0x1",
"Random4kReadTypicalNanoSeconds": 34534345348,
"UnallocatedNVMNamespaceCapacityBytes": 5497558138880,
"OptimalWriteSizeBytes": 512
},
"Capacity": {
"Data": {
"AllocatedBytes": 10995116277760,
"ConsumedBytes": 5497558138880
}
},
"AllocatedVolumes": {
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Storage/FabricAttachArray/StoragePools/NVMeSet1/AllocatedVolumes"
}
}| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Name | NVM Spec Property / Field: NVMSETID NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 16-bit value Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 01:00 |
| Description | The name of the resource or array member. | |
| LongDescription | This object represents the name of this resource or array member. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. This string value shall be of the ‘Name’ reserved word format. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | In Redfish, Name is a read-only field. | Map the NVMSETID field to a string with the format: “0xABCD” |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Description | NVM Spec Property / Field: N/A |
| Type | String | N/A |
| Description | The description of this resource. | See note below. |
| LongDescription | This object represents the description of this resource. The resource values shall comply with the Redfish Specification-described requirements. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | In Redfish, Description is a read-only field. | Return the common description: “An NVM Set is a collection of NVM that is separate (logically and potentially physically) from NVM in other NVM Sets. One or more namespaces may be created within an NVM Set and those namespaces inherit the attributes of the NVM Set. A namespace is wholly contained within a single NVM Set and shall not span more than one NVM Set.” |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.State | NVM Spec Property / Field: N/A |
| Type | Resource.State (enum) | N/A |
| Description | The known state of the resource, such as, enabled. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall indicate whether and why this component is available. Enabled indicates the resource is available. Disabled indicates the resource has been intentionally made unavailable but it can be enabled. Offline indicates the resource is unavailable intentionally and requires action to make it available. InTest indicates that the component is undergoing testing. Starting indicates that the resource is becoming available. Absent indicates the resource is physically unavailable. | |
| Mandatory | Do not implement. | |
| Notes | Possible values: Enabled / Disabled / StandbyOffline / StandbySpare / InTest / Starting / ABsent / UnavaialableOffline / Deferring / Quiesced / Updating / Qualified | There is not a clear mapping for State of an NVM Set. Do not implement this property. |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Status.Health | NVM Spec Property / Field: N/A |
| Type | Resource.Health | N/A |
| Description | The health state of this resource in the absence of its dependent resources. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall represent the health state of the resource without considering its dependent resources. The values shall conform to those defined in the Redfish Specification. | |
| Mandatory | Do not implement. | |
| Notes | Possible Values: OK / Warning / Critical | There is not a clear mapping for health of an NVM Set. Do not implement this property. |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.ConsumedBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: Total NVM Set Capacity, Unallocated NVM Set Capacity NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: bytes Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 31:16 for Total NVM Set Capacity |
| Byte 47:32 for Unallocated NVM Set Capacity. | ||
| Description | The maximum number of bytes that can be allocated in this data store for this data type. | |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the maximum number of bytes that can be allocated in this data store for this data type. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | This is calculated as “Total NVM Set Capacity” - “Unallocated NVM Set Capacity”. |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | Capacity.Data.AllocatedBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: Total NVM Set Capacity NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: bytes Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 31:16 for Total NVM Set Capacity |
| Description | The number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | |
| LongDescription | The value shall be the number of bytes currently allocated by the storage system in this data store for this data type. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | AllocatedVolumes | NVM Spec Property / Field: |
| Type | VolumeCollection.VolumeCollection | |
| Description | A reference to the collection of volumes allocated from this storage pool. | |
| LongDescription | The value of this property shall contain a reference to the collection of volumes allocated from this storage pool. | |
| Mandatory | Mandatory | |
| Notes | A pointer to the set of namespaces allocated from this NVM Set. | The allocated volumes contains pointers to the allocated volumes objects. These are the set of namespaces created from this NVM Set. |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeSetProperties.SetIdentifier | NVM Spec Property / Field: NVMSETID NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 16-bit value Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 01:00 |
| Description | A 16-bit hex value that contains the NVMe Set identifier. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a 16-bit hex value that contains the NVMe Set identifier. The NVM Set identifier is unique within a subsystem. Reserved values include 0. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Return as hex value as described in the Swordfish schema. |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeSetProperties.OptimalWriteSizeBytes | NVM Spec Property / Field: OptimalWriteSize NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: Bytes Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 15:12 |
| Description | This property contains the Optimal Write Size in Bytes for this NVMe Set. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the Optimal Write Size in Bytes for this NVMe Set. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeSetProperties.EnduranceGroupIdentifier | NVM Spec Property / Field: EnduranceGroupIdentifier NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | String | NVM Spec Property Type: 2 bytes Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 03:02 |
| Description | A 16-bit hex value that contains the endurance group identifier. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain a 16-bit hex value that contains the endurance group identifier. The endurance group identifier is unique within a subsystem. Reserved values include 0. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes |
| Redfish/Swordfish | NVMe / NVMe-oF | |
|---|---|---|
| Property | NVMeSetProperties.Random4kReadTypicalNanoSeconds | NVM Spec Property / Field: Random 4 KiB Read Typical NVM Spec: Section:Figure NVMe 1.4a: Section 5.15.2.5, Figure 253: NVM Set Attributes Entry |
| Type | Int64 | NVM Spec Property Type: 4 bytes Additional NVM Spec Identifying Information: ByteOffset: 11:08 |
| Description | Indicates the typical time to complete a 4k read in 100 nano-second units when the NVM Set is in a Predictable Latency Mode Deterministic Window and there is 1 outstanding command per NVM Set. | |
| LongDescription | This property shall contain the typical time to complete a 4k read in 100 nano-second units when the NVM Set is in a Predictable Latency Mode Deterministic Window and there is 1 outstanding command per NVM Set. | |
| Mandatory | ||
| Notes | Convert from 100 nanosecond units to nanosecond units. |