Overview

Introduction
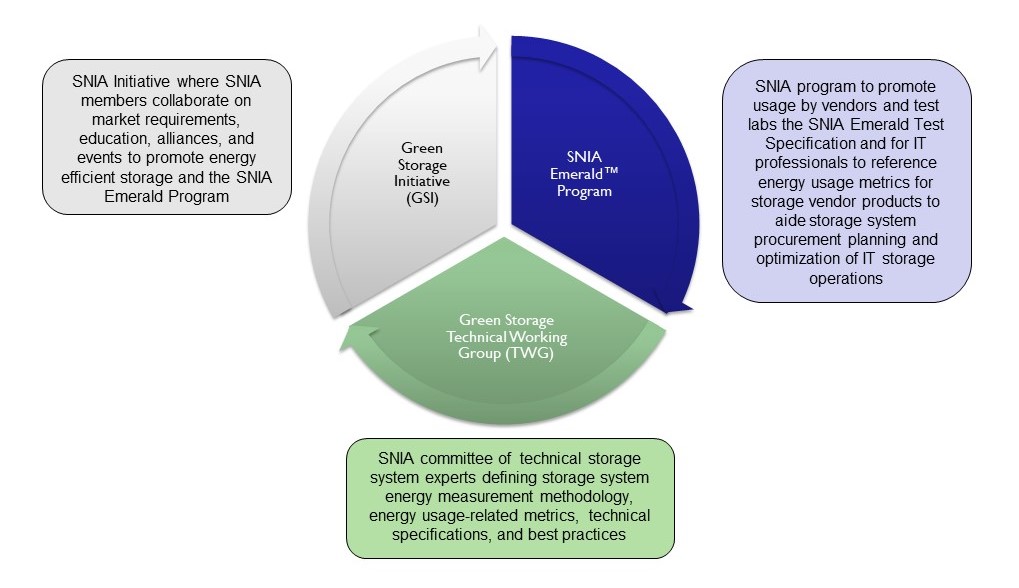
The Storage Networking Industry Association’s (SNIA) Green Storage Initiative (GSI) is dedicated to advancing energy efficiency for networked storage systems through best practices and energy measurement metrics. The SNIA’s Green Storage activities are coordinated and delivered through the SNIA Green Storage Technical Working Group (TWG) and the Green Storage Initiative. The GSI is responsible for market development and adoption of the SNIA Emerald™ Program, IT industry requirements for the Green Storage TWG technical specifications, and cross-industry alliances and relationships with national bodies energy programs, standards bodies, and energy testing services.
The SNIA Emerald™ Program and the SNIA Emerald™ Power Efficiency Measurement Specification
The SNIA Emerald™ Program provides an envelope of activities and elements that further advance the use of storage system measurement procedures and test metrics as documented in the SNIA Emerald™ Power Efficiency Measurement Specification. Activities include:
Periodic comprehensive industry training on how to prepare and test a storage system for vendors and independent test labs;
Joint industry stakeholder meetings with regulatory bodies for the reference and use of Power Efficiency Specification;
Elevating awareness of industry and national regulatory testing programs and analysis of submitted test reports;
Cross-industry alliances for testing tools, methods, and policy setting recommendations.
Relationship with the USA Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ENERGY STAR Program
The SNIA Emerald Specification is a building block for national and regulatory testing programs driving energy efficiency. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Energy Star Program for Data Center Storage references the SNIA Emerald Specification and publishes storage vendor system test reports for public use to aide IT procurement, IT planning, and IT operations.
“The EPA ENERGY STAR program is very supportive of the SNIA work on the storage system taxonomy and the test measurement methods contained within the SNIA Emerald Power Efficiency Measurement Specification,” said Robert J. Meyers, Data Center Products Lead, EPA ENERGY STAR. “They form an excellent starting point in the industry effort to understand and improve storage system energy efficiency. Additionally, the data generated using the Emerald test method will help drive a wider industry discussion on energy efficiency, testing methods, and efficiency metrics.”
The SNIA Emerald™ Program
The SNIA Emerald™ Program is the focal point for the industry for SNIA Emerald™ Power Efficiency Measurement Specification and technical training for the SNIA Emerald™ test methodology.
Storage vendors can download the SNIA Emerald™ Power Efficiency Measurement Specification and accompanying User Guide from the SNIA Emerald™ website. Vendors and test labs can then test products and analyze the results in accordance with the SNIA Emerald™ Specification. Test results may be submitted to a regulatory body, per that body’s specified reporting format and testing requirements.
The SNIA Emerald™ Power Efficiency Measurement Specification consists of the following elements:
Taxonomy: An industry-wide way of segmenting storage systems for products that span the range from consumer solutions to enterprise configurations used to categorize the test results.
Test Methodology: A detailed and consistent means of testing various types of storage systems with load generators and power measurement instruments.
Test Metrics - Idle Measurement Test: The idle test applies to storage systems and components which are configured, powered up, connected to one or more hosts, and capable of satisfying externally- and application level-initiated IO requests within normal response time constraints.
Test Metrics - Active Measurement Test: Testing of storage products and components is said to be in an active state when they are processing externally-initiated, application level requests for data transfer between a host(s) and the storage product(s).






